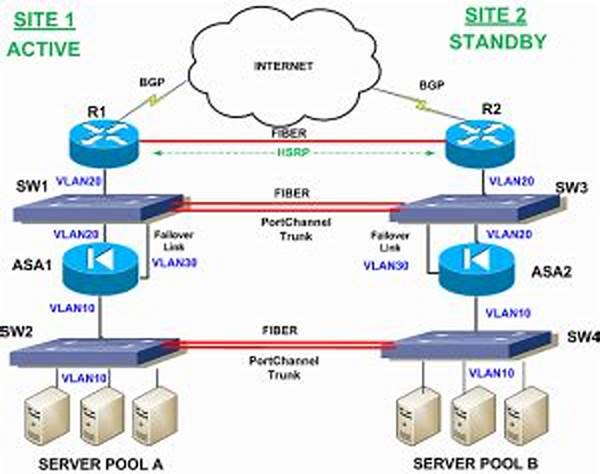
In the increasingly digitized world, the importance of stable and continuous network service cannot be overstated. As businesses and organizations rely heavily on network operations for daily functions, the implementation of strategies like network redundancy and failover becomes pivotal. These mechanisms act as a safety net, ensuring that network services remain viable and operative, even in the face of disruptions. Through network redundancy and failover, businesses can safeguard against potential losses that might arise due to network failures, thereby maintaining operational integrity and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Understanding Network Redundancy and Failover
Network redundancy involves the duplication of critical components or functions within a network as a precaution against potential failures. By having backup systems in place, organizations can ensure continuous network availability. On the other hand, failover is a complementary process where, upon detecting network malfunctions, operations are swiftly transitioned to backup systems. This seamless switch to an alternative network path or system ensures minimal interruption in service. Effective implementation of network redundancy and failover requires meticulous planning and investment but pays off by significantly enhancing network reliability and customer trust.
For contemporary businesses, network redundancy and failover are not merely options; they are essential components of a robust IT strategy. These mechanisms take center stage in disaster recovery plans, offering peace of mind in an era where network downtime can have critical consequences. Factoring in both hardware and software redundancy can cover a broader spectrum of potential issues, ensuring that every conceivable point of failure is addressed. In doing so, network redundancy and failover extend beyond mere technical solutions, representing a commitment to reliability and resilience.
Components of An Effective Strategy
1. Multiple Data Paths: Establishing several data pathways exemplifies network redundancy, preventing single point failures and ensuring multiple routes remain available.
2. Automatic Failover Systems: Automated systems swiftly detect failures and initiate failover mechanisms, maintaining uninterrupted service and operational continuity.
3. Regular Testing Protocols: Scheduled tests are vital for assessing the performance of redundancy and failover systems, unveiling potential vulnerabilities to be rectified.
4. Redundant Hardware: Employing duplicate hardware components across the network avoids dependency on a single device, enhancing reliability and failover capacity.
5. Software Solutions: Advanced software systems orchestrate network redundancy and failover strategies efficiently, ensuring seamless transition during network outages.
Implementing a Redundancy Plan
The implementation of a redundancy plan necessitates a strategic approach to align organizational needs with technical capabilities. Establishing a comprehensive redundancy infrastructure lays the foundation for effective network management. Key steps involve identifying critical network components and assessing potential risks associated with network downtime. Organizations should invest in both hardware and software solutions to minimize the risk of data loss and ensure service availability.
Developing a thorough failover strategy is integral to a successful redundancy plan. This involves deciding how operations will transition to backup systems in case of primary system failures. By considering various failover scenarios, companies can chart out procedures to ensure a smooth switch, thereby mitigating the impact of any disruptions. The commitment to network redundancy and failover underscores an organization’s dedication to maintaining continuous service and supporting long-term business sustainability.
Importance in Modern Networks
The critical role of network redundancy and failover has gained prominence in modern networks, given the escalating reliance on digital operations. These strategies provide solutions to anticipated network failures, helping organizations maintain efficiency and upholding customer service standards. Their relevance is reflected in the increased risk of downtime-related consequences, including financial losses and diminished reputation, especially for sectors heavily reliant on digital infrastructure.
Network redundancy and failover are integral in ensuring business continuity, especially in the face of unexpected incidents such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks. Robust redundancy strategies not only accommodate potential network hurdles but also fortify cybersecurity measures. By ensuring network reliability, organizations can foster growth and provide stakeholders assurance in their operations, emphasizing the indispensable nature of these strategies.
Challenges in Implementation
Instituting network redundancy and failover presents several challenges, primarily concerning cost implications and technical complexities. Establishing redundancy infrastructures involves procuring additional resources, which may strain budgets, particularly for smaller enterprises. Moreover, the intricacies involved in designing and integrating failover systems necessitate technical expertise, which might not be readily available in-house.
Furthermore, managing the dynamic needs of an organization alongside stability goals presents coordination challenges. Aligning network redundancy and failover strategies with evolving operational requirements demands ongoing adjustments and fine-tuning. Despite these obstacles, the investment in redundancy infrastructure is necessary. Addressing these challenges requires long-term planning and robust IT support to achieve desired resilience outcomes.
Assessing Network Redundancy
A critical aspect of maintaining effective network redundancy and failover systems is regular evaluation and monitoring. Organizations must continuously assess the adequacy of their redundancy measures to meet evolving demands. This entails reviewing existing protocols and considering scalability options to accommodate growth. Through continual assessment, businesses can enhance system resilience and avoid potential oversights.
Moreover, leveraging data analytics to evaluate performance metrics assists in refining redundancy strategies, highlighting areas requiring optimization. These evaluations should include testing failover protocols to ensure operational seamlessness during actual disruptions, enabling prompt corrective measures. Through diligence in assessment, network redundancy and failover systems can remain robust and responsive to unforeseen challenges, allowing organizations to preserve reliability standards.
Summary of Network Redundancy and Failover
In summarizing the concepts of network redundancy and failover, their significance in modern networking frameworks is apparent. Establishing reliable networks capable of withstanding adversity is essential for organizations aiming to maintain competitive advantages and uphold customer trust. With proactive redundancy strategies, businesses can mitigate disruptions’ impacts and ensure consistent service delivery, reinforcing their operational frameworks.
Comprehensive redundancy planning goes hand in hand with strategic failover systems, which automate responses to network anomalies and redirect operations to alternative pathways swiftly. The resulting enhancements in service reliability directly contribute to organizational longevity and efficiency. By addressing both technical and strategic dimensions, network redundancy and failover strategies solidify organizational commitment to network resilience, ensuring sustained business operations amidst an ever-evolving technological landscape.