The importance of accessibility in digital resources cannot be overstated. In the contemporary digital landscape, ensuring that digital resources are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities, is a fundamental responsibility of organizations. In this regard, metrics for digital resource accessibility serve as essential tools to measure, assess, and improve the accessibility of web content, applications, and digital documentation. These metrics provide tangible insights into how effectively digital resources are being made available to users with varying needs, helping to ensure inclusivity and compliance with established accessibility standards.
Understanding the Metrics for Digital Resource Accessibility
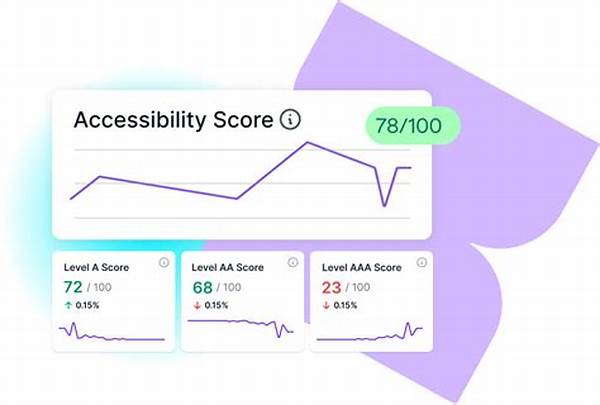
Metrics for digital resource accessibility encompass a wide range of parameters that evaluate both the technical and experiential aspects of accessibility. These metrics include, but are not limited to, aspects like the compatibility of a website with screen readers, the use of alternative text for images, appropriate color contrast, keyboard navigability, and the logical structuring of content. By systematically analyzing these factors, organizations can pinpoint areas of improvement and implement strategies to make their resources more inclusive. The integration of metrics for digital resource accessibility into routine evaluations ensures that accessibility remains a dynamic and ongoing priority, rather than a static or one-time task. This commitment is vital for achieving the broader goal of digital inclusion, which empowers individuals with disabilities to participate fully in the digital age.
Key Components of Digital Resource Accessibility Metrics
1. Screen Reader Compatibility: This metric evaluates how well digital resources function with screen reading software, essential for visually impaired users.
2. Alternative Text Usage: It assesses whether images and non-text elements are equipped with descriptive alt texts to provide context for those relying on screen readers.
3. Color Contrast Adequacy: This ensures text visibility against background colors, central to maintaining readability for individuals with visual impairments.
4. Keyboard Navigability: The metric examines if users can navigate a website solely using a keyboard, crucial for individuals with motor disabilities.
5. Logical Content Structure: It evaluates the proper organization of content through headings and landmarks, aiding users in comprehending and accessing information seamlessly.
Implementing Effective Accessibility Metrics
The successful implementation of metrics for digital resource accessibility requires a structured approach. Organizations must begin by establishing a comprehensive framework that addresses all relevant accessibility aspects, tailored to specific digital environments. Incorporating metrics for digital resource accessibility into the development and maintenance processes ensures that digital platforms are designed with inclusivity in mind from the outset. Additionally, regular audits using these metrics help maintain conformity with accessibility standards and adapt to evolving technologies and user needs. By prioritizing accessibility metrics at every stage, companies can cultivate a more inclusive digital ecosystem that benefits all users.
Challenges in Measuring Accessibility
Successfully quantifying metrics for digital resource accessibility involves several challenges. One of the predominant obstacles is the constant evolution of technology, which necessitates ongoing updates to metrics to encompass new digital formats and tools. Moreover, the subjective nature of users’ accessibility experiences can complicate quantitative assessments. Despite these challenges, the consistent application of defined metrics provides a foundation upon which organizations can base their accessibility improvements. By investing in the development and refinement of these metrics, companies can overcome challenges effectively, ensuring that accessibility remains an integral part of their digital strategy.
The Role of Stakeholders
In the establishment of metrics for digital resource accessibility, collaboration among stakeholders is paramount. Organizations, developers, accessibility experts, and users must work together to identify and enforce appropriate metrics. This cooperative effort ensures that the metrics are not only comprehensive but also practical and user-centered. Accessibility metrics derived from stakeholder input are more likely to be aligned with actual user needs and effectively bridge the gap between technical requirements and user experience. By fostering collaboration, organizations can achieve meaningful progress toward digital accessibility objectives.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Metrics for digital resource accessibility are not static; they should evolve alongside technological advancements and user feedback. Continuous improvement and monitoring involve regular reassessment and updates to the metrics, aligning them with the latest accessibility standards and guidelines. This iterative process ensures that digital resources remain accessible and relevant to all users, fostering an environment of inclusion and participation. Organizations that commit to ongoing monitoring can proactively address accessibility challenges, thus maintaining their dedication to digital inclusivity.
Conclusion: The Future of Digital Accessibility Metrics
In summary, metrics for digital resource accessibility are indispensable for promoting inclusivity in digital spaces. By addressing technical, experiential, and stakeholder-involved aspects of accessibility, these metrics create a framework for continuous improvement. Future developments will likely refine and expand these metrics, integrating emerging technologies and methodologies to meet the evolving needs of users. Organizations that prioritize these metrics not only comply with legal and ethical standards but also contribute to a more equitable digital environment. As digital accessibility gains prominence, the role of accessibility metrics will be crucial in guiding organizations toward a future where digital content is truly accessible to all.