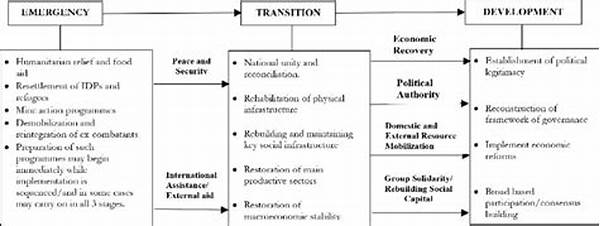
In the aftermath of conflicts, affected nations face the daunting task of rebuilding and healing. The process of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery is crucial for establishing peace, reconstructing infrastructure, and revitalizing economies. This multifaceted endeavor requires coordinated efforts from governmental bodies, international organizations, and local communities.
The Significance of Comprehensive Planning in Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
Post-conflict reconstruction and recovery represent pivotal phases in a country’s journey towards sustainable peace and development. To lay a solid foundation for future growth, comprehensive planning must be implemented. This involves assessing immediate needs such as the restoration of essential services, repairing damaged infrastructure, and providing humanitarian aid. Longer-term strategies must also be devised, prioritizing institutional reforms, fostering educational opportunities, and stimulating economic growth. The intricate interplay of social, political, and economic elements necessitates a holistic approach, ensuring that all facets of society are addressed in order to prevent a relapse into conflict. Furthermore, the active involvement of local populations is vital to ensure that the reconstruction reflects the community’s aspirations and values. As such, a thorough understanding of the indigenous cultural, social, and political context is paramount. International assistance plays a supportive role, providing financial resources and expertise, yet the ultimate success hinges on locally-driven initiatives. In essence, post-conflict reconstruction and recovery are not merely about rebuilding physical structures but redefining societal frameworks to support lasting peace.
Key Elements of Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
1. Restoration of Law and Order: Establishing a functional legal and justice system is critical in post-conflict reconstruction and recovery. This ensures rights are protected and justice is administered fairly.
2. Economic Revitalization: Stimulating the economy through investment and job creation facilitates sustainable post-conflict reconstruction and recovery by empowering communities and reducing poverty levels.
3. Social Cohesion and Reconciliation: Fostering social unity and reconciliation among previously conflicting factions is essential for achieving lasting peace during the post-conflict reconstruction and recovery phase.
4. Infrastructure Rebuilding: Reconstructing transportation, communication, and utility networks is necessary for functional post-conflict reconstruction and recovery, enabling communities to regain normalcy and productivity.
5. Educational Development: Prioritizing education ensures the nurturing of informed citizens equipped to participate actively in governance and development, thus reinforcing post-conflict reconstruction and recovery efforts.
Challenges in Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
The process of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery is inherently complex and fraught with numerous challenges. One primary challenge is maintaining security and preventing a recurrence of conflict while rebuilding takes place. Establishing a sense of security is essential for displaced populations to return and for economic activities to resume. Another significant hurdle is addressing the societal divisions that conflicts inevitably exacerbate. Efforts must be made to foster reconciliation and build bridges between communities, ensuring that past grievances do not hinder future progress. Furthermore, the presence of unexploded ordnance and landmines poses significant risks to personal safety and development efforts, necessitating comprehensive clearance initiatives.
In addition, there is the challenge of coordination among various stakeholders, including international donors, government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and local communities, to ensure synergistic efforts and avoid duplicative resources. The need for capacity building is also stark, as local institutions and personnel often require substantial strengthening to handle the associated duties of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery sustainably. Additionally, financing these endeavors remains a critical issue, necessitating innovative funding mechanisms and ensuring transparency and accountability in resource allocation. Navigating these complexities requires a pragmatic approach focused on adaptability, resilience, and sustained political commitment.
Strategies for Effective Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
1. Community Participation: Involving local communities in decision-making processes ensures that post-conflict reconstruction and recovery initiatives are culturally relevant and sustainable.
2. Institutional Strengthening: Building robust institutions capable of effective governance is fundamental for the success of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery.
3. International Cooperation: Engaging international partners provides essential support through funding, expertise, and diplomatic backing for post-conflict reconstruction and recovery efforts.
4. Sustainable Development Goals Alignment: Aligning efforts with the Sustainable Development Goals ensures that post-conflict reconstruction and recovery strategies contribute to broader global priorities.
5. Innovative Financing Models: Utilizing diverse financing models, including public-private partnerships, can enhance the resources available for post-conflict reconstruction and recovery.
6. Gender Inclusivity: Ensuring gender parity in planning brings diverse perspectives and fosters gender equality as part of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery.
7. Capacity Building: Emphasizing training and education enhances the ability of local institutions to manage post-conflict reconstruction and recovery processes effectively.
8. Conflict Sensitivity: Applying a conflict-sensitive lens in planning minimizes tensions and supports harmonious post-conflict reconstruction and recovery.
9. Monitoring and Evaluation: Systematic monitoring and evaluation ensure that post-conflict reconstruction and recovery programs are adaptive and goal-oriented.
10. Long-term Commitment: Long-term advocacy is crucial as post-conflict reconstruction and recovery need sustained efforts far beyond the immediate aftermath of conflict.
The Role of Governance in Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
Governance plays a pivotal role in executing effective post-conflict reconstruction and recovery plans. The re-establishment of credible governance institutions is essential to restore public trust and confidence. This process involves rebuilding and reforming governmental bodies to ensure transparency, accountability, and responsiveness to citizen needs. Efficient governance also provides a framework for law and order, enabling the legal system to address past injustices and foster reconciliation among divided communities. Moreover, strong governance structures facilitate the coordination among diverse stakeholders engaged in reconstruction efforts, from international organizations to local grassroots agencies, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and ethically.
Furthermore, governance systems bolster economic development by creating an environment conducive to investment and growth, crucial for long-term stability and prosperity. The empowerment of local governments and decentralization of administrative functions can ensure that post-conflict reconstruction and recovery efforts are tailored to local needs and capacities. Additionally, the promotion of inclusive governance by integrating underrepresented groups, particularly women and minorities, into decision-making processes reinforces social cohesion and resilience. Thus, a robust governance framework lays the foundation for transformative post-conflict reconstruction and recovery, steering nations towards a peaceful and prosperous future.
The Economic Dimension of Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
Economic stability is a cornerstone of successful post-conflict reconstruction and recovery. The revitalization of the economy facilitates the generation of jobs, diminishes poverty, and enables communities to become self-sufficient. Restoring financial institutions, reforming economic policies, and attracting investment are crucial steps in rebuilding a robust economy. Infrastructure development, including transportation, communication, and energy systems, is integral in attracting businesses and ensuring efficient resource distribution. Furthermore, supporting the private sector, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises, can spur innovation and growth.
In post-conflict settings, addressing the informal economy is equally important, as it often represents a significant portion of economic activity. Formalizing and enhancing this sector can increase job opportunities and broaden the economic base. Moreover, inclusive economic policies that empower marginalized groups, such as women and youth, contribute to equitable growth and social stability. International aid and investment play instrumental roles, providing necessary capital and expertise, but it is the strategic planning and inspired leadership within the nation that ultimately drive sustainable economic revitalization. In sum, a focus on economic renewal embedded in comprehensive post-conflict reconstruction and recovery strategies ensures a transition from fragility to resilience.
Summary of Post-Conflict Reconstruction and Recovery
In summary, post-conflict reconstruction and recovery encapsulate a series of strategic actions aimed at restoring peace, rebuilding infrastructure, and fostering sustainable development in nations transitioning from conflict. This complex process requires a multifaceted approach, addressing immediate relief needs and long-term development goals. One of the critical components involves rebuilding governmental structures and establishing rule of law to provide a foundation for stability and public trust.
Moreover, the revitalization of the economy is imperative. By creating jobs and stimulating economic growth, nations can mitigate poverty and foster self-sufficiency among their populations. Social healing and reconciliation form another core aspect of recovery strategies, promoting unity and understanding among previously conflicting communities. Across these dimensions, international collaboration and local participation are crucial, with both international bodies and local communities playing vital roles in ensuring that initiatives align with cultural contexts and meet the actual needs of the affected populations. Ultimately, the success of post-conflict reconstruction and recovery hinges on sustained effort, political will, and the commitment to transforming adversity into opportunities for lasting peace and development.