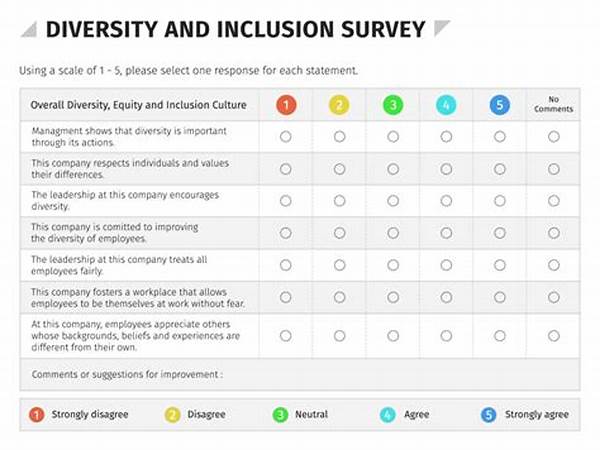
The advent of digital technology has ushered in a new era of data collection, primarily through online surveys. However, to ensure that these surveys are effective and equitable, there is a pressing need to incorporate inclusive design principles. Inclusive Online Survey Design Guidelines are crucial to making sure that all participants, regardless of their abilities or backgrounds, can access and complete surveys without hindrance. This approach not only amplifies the diversity of data collected but also enhances the credibility of the findings obtained. By adhering to these guidelines, researchers and organizations can foster a more representative and accurate understanding of their target populations.
Importance of Inclusive Online Survey Design
The essence of inclusive online survey design guidelines lies in acknowledging and addressing the diverse needs of survey participants. These guidelines ensure that surveys are accessible to everyone, including individuals with disabilities, varying literacy levels, and different cultural backgrounds. By embracing inclusivity, organizations can access a broader range of perspectives, contributing to more comprehensive research outcomes. Furthermore, these guidelines help eliminate biases that might arise from a limited demographic reach, thereby elevating the validity and reliability of survey results. In practice, applying inclusive design principles involves considering factors such as language simplicity, visual accessibility, and digital compatibility, ensuring that these elements align with the varied needs of the survey audience. Ultimately, inclusive online survey design guidelines facilitate equitable participation, fostering genuine engagement and response accuracy from all demographics, which is paramount for meaningful analysis and decision-making.
Key Principles of Inclusive Survey Design
1. Accessibility: Ensuring surveys are accessible to individuals with disabilities is a cornerstone of inclusive online survey design guidelines. This includes compatibility with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
2. Simplicity: Crafting simple, clear language reduces barriers for individuals with varied literacy levels. This aligns with inclusive online survey design guidelines by making information digestible and comprehensible.
3. Cultural Sensitivity: Including diverse cultural perspectives fulfills inclusive online survey design guidelines. It ensures questions are respectful and relevant across different cultural contexts, avoiding potential biases.
4. Technological Compatibility: Ensuring surveys work seamlessly across various devices and internet speeds is central to inclusive online survey design guidelines. This guarantees broad access regardless of participants’ technological resources.
5. Privacy and Consent: Respecting participants’ privacy through clear consent processes is fundamental under inclusive online survey design guidelines, fostering trust and encouraging honest and complete responses.
Implementing Inclusive Online Survey Design
Incorporating inclusive online survey design guidelines requires a strategic commitment to understanding and addressing the barriers potential respondents might face. This involves extensive pre-survey testing, in which different user groups examine survey prototypes and provide feedback on accessibility and clarity. Such an iterative testing approach helps identify unintentional design limitations, allowing for corrective measures before wide-scale deployment. Additionally, continuous monitoring and evaluation of survey implementations offer insights into user experiences, enabling ongoing refinements based on real-time feedback. Organizations can benefit considerably from adopting a participant-centric mindset, fostering inclusivity throughout the survey design and execution process. Moreover, training staff to recognize and mitigate biases furthers the mission of achieving a genuinely inclusive survey environment.
Challenges and Solutions
The adoption of inclusive online survey design guidelines is not without its challenges. One primary issue is the resource-intensive nature of designing and testing surveys that accommodate a wide array of user needs. However, this obstacle can be mitigated through the use of specialized software and tools that automate accessibility checks. Another challenge is balancing simplicity with depth in survey content, ensuring questions are both straightforward and comprehensive. A solution here is collaborative design workshops with diverse stakeholders to gather insights on clarity and relevance. Time constraints can also pose difficulties, yet strategic prioritization and phased implementation can alleviate such pressures. Ultimately, organizations must remain committed to these guidelines, understanding that the benefits of inclusive survey design far outweigh the challenges. Embracing inclusive principles enhances data quality and supports the equitable participation of all prospective respondents.
Best Practices for Survey Developers
Survey developers aiming to adhere to inclusive online survey design guidelines must be proactive in their approach to design and implementation. Engaging with an array of subject matter experts, including accessibility professionals and cultural consultants, is vital to crafting feasible and informed survey frameworks. A focus on visual design that prioritizes contrast, readability, and intuitive navigation can significantly improve respondent engagement and accuracy. Moreover, leveraging inclusive communication strategies—like providing alternative text for images and offering survey questions in multiple languages—expands reach and inclusivity. Testing surveys with real users offers valuable perspectives, guiding enhancements that cater to the actual experiences of diverse populations. Finally, embracing a continuous learning mindset, adaptively refining survey protocols based on evolving user feedback and technological advances, ensures sustained adherence to inclusive online survey design guidelines.
Evaluating Success of Inclusivity Efforts
The success of inclusive online survey design guidelines can be measured through both qualitative and quantitative metrics. Feedback from participants can provide qualitative insights into their experiences, highlighting areas where guidelines effectively met user needs or where potential improvements exist. Quantitatively, analyzing completion rates across diverse demographics can reveal the inclusivity impact on participation scope. Furthermore, monitoring the diversity of responses attained through demographic analysis helps ascertain the broader reach achieved by the survey. The ultimate goal is fostering an inclusive data collection framework that empowers every participant’s voice to be heard and valued, enriching the quality and depth of insights gathered. By consistently applying a robust evaluation framework, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to inclusivity, aligning strategic objectives with equitable practices in collecting valuable, comprehensive data.
Summary and Future Directions
In conclusion, inclusive online survey design guidelines are indispensable for ensuring that surveys are accessible, relevant, and respectful to all potential respondents. They encapsulate a commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusivity, principles that are increasingly recognized as vital in today’s global research landscape. By facilitating broader participation, these guidelines contribute to more robust and nuanced data, enriching scientific, academic, and commercial insights. Looking forward, organizations must remain committed to evolving these practices. Engaging with new technologies and methodologies offers opportunities to further refine and enhance inclusivity efforts. Collaborative partnerships and ongoing research into best practices will serve as valuable assets in this endeavor. As the digital space expands, the adherence to inclusive online survey design guidelines not only remains a vital consideration but a moral imperative, ensuring that every voice has the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to the collective knowledge pool.