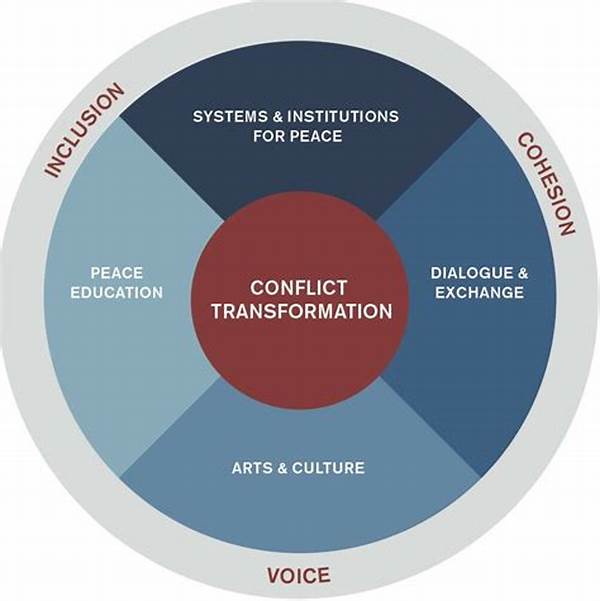
Understanding Conflict Transformation Frameworks
Conflict transformation frameworks are methodologies employed to address the underlying causes of conflicts and to foster long-lasting peace. Unlike traditional conflict resolution techniques, which often aim to stop violence through compromise or agreement, conflict transformation strives for a deeper change in the structure and relationships involved in the conflict. This approach acknowledges that conflicts are inevitable in human interactions but sees them as opportunities for constructive change rather than being solely negative phenomena.
The central tenet of conflict transformation frameworks is that conflicts are systemic issues that require systemic solutions. This means they not only focus on immediate problems but also address long-term relational and structural issues that contribute to the recurrence of conflict. Such a comprehensive approach seeks to change perceptions, attitudes, and social and political structures that sustain conflicts. Tools and techniques under these frameworks often include dialogue facilitation, trust-building exercises, and collaborative problem-solving initiatives.
By addressing the root causes of conflict, conflict transformation frameworks aim to create enduring peace by transforming the relationships and social structures that underpin the conflicts. These frameworks are applied in various contexts, such as community disputes, national peacemaking processes, and international relations. This holistic approach challenges parties to reframe their perspectives and work together towards a shared future, fostering resilience and reconciliation in the fabric of society.
Essential Components of Conflict Transformation Frameworks
1. Holistic Approach: Conflict transformation frameworks emphasize a comprehensive approach to conflict management, addressing the systemic and relational factors that contribute to conflict. This ensures peace efforts are sustainable and not merely temporary solutions.
2. Long-Term Goals: These frameworks prioritize long-term transformation over short-term peace agreements, recognizing the necessity of addressing deeper social, economic, and political issues that fuel conflicts.
3. Inclusivity: In conflict transformation frameworks, inclusivity is critical, ensuring that all stakeholders, especially marginalized groups, are part of the peacebuilding process. This reduces the likelihood of future conflicts by ensuring equitable representation.
4. Relationship Building: Developing and nurturing relationships among conflicting parties is central to conflict transformation frameworks. These frameworks facilitate trust-building activities that help change adversarial relationships into cooperative ones.
5. Empowerment and Ownership: Conflict transformation frameworks empower local communities to take ownership of the peace process, encouraging active participation and fostering a sense of responsibility and commitment to achieve enduring peace.
The Role of Dialogue in Conflict Transformation Frameworks
Dialogue plays a pivotal role in conflict transformation frameworks by facilitating open communication and understanding between conflicting parties. These frameworks employ dialogue as a tool to promote empathy and mutual respect, essential components for transforming relationships. In many cases, dialogue involves structured conversations that help surface underlying issues, allowing parties to explore their differences and commonalities. Through facilitated dialogues, participants can express grievances, share narratives, and develop a shared vision for the future.
Moreover, conflict transformation frameworks utilize dialogue to break down stereotypes and build trust. By creating a safe environment for discussion, parties can explore innovative solutions to their conflicts, shifting from positions of power to positions of collaboration. Dialogue aids in the process of re-humanizing opponents, which is vital in transforming adversarial dynamics into collaborative and peaceful relationships.
Overall, dialogue as part of conflict transformation frameworks serves as a bridge between conflicting entities, creating the groundwork for sustainable peace efforts. It enables the voices of all stakeholders to be heard and recognized, providing a space where inclusive and comprehensive solutions to complex conflicts can emerge.
Practical Applications of Conflict Transformation Frameworks
To apply conflict transformation frameworks effectively, practitioners must adopt a series of strategic actions and processes:
1. Initial Assessment: Analyze the origins, dynamics, and impact of the conflict to choose appropriate strategies.
2. Engagement and Negotiation: Involve all relevant stakeholders in dialogue to explore solutions collaboratively.
3. Implementation of Change Strategies: Initiate changes in social and political structures that contribute to conflict.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly review the process and impact to ensure adaptive strategies and continuous improvement.
5. Capacity Building: Strengthen the ability of local communities and organizations to manage and resolve conflicts independently.
6. Communication and Advocacy: Promote public awareness and engagement in the peace process, supporting sustained transformation.
7. Conflict-Sensitive Development: Design and implement development programs that reduce inequalities and prevent future conflicts.
8. Restorative Justice: Employ practices that address past grievances and promote healing and reconciliation.
9. Cultural Sensitivity: Integrate local customs and traditions into the peace process to ensure cultural compatibility and acceptance.
10. Sustainability Measures: Develop mechanisms for ongoing support and resource allocation to sustain peace efforts.
Challenges in Implementing Conflict Transformation Frameworks
Implementing conflict transformation frameworks presents several challenges, including entrenched power dynamics, resistance from stakeholders, and the complexity of systemic change. The deeply rooted nature of many conflicts can make transformation efforts arduous and time-consuming, as shifting long-standing perceptions requires perseverance and dedication.
Another challenge is the inclusivity of the process. While conflict transformation frameworks emphasize the need for broad participation, including marginalized voices can be difficult due to logistical, cultural, or political barriers. Ensuring equal representation and participation in dialogue and decision-making processes is essential but often requires innovative strategies to overcome these obstacles.
Furthermore, measuring the success of conflict transformation frameworks poses significant challenges. Unlike traditional conflict resolution, where clear-cut results such as ceasefires indicate success, transformation requires ongoing assessment over an extended period. The dynamic nature of conflicts demands that frameworks remain flexible and responsive to changing conditions, complicating the evaluation of their effectiveness.
Best Practices for Conflict Transformation Frameworks
Adopting best practices is crucial for the success of conflict transformation frameworks. These practices include fostering an environment of mutual respect and understanding, where parties are encouraged to communicate openly and without fear. Practitioners should prioritize empathy and active listening to understand better each party’s perspectives and grievances.
The adoption of culturally sensitive approaches ensures that conflict transformation frameworks are relevant and acceptable to local communities. This cultural adaptability is vital for gaining the trust and cooperation of stakeholders who might otherwise be resistant to external interventions.
Additionally, conflict transformation frameworks benefit from incorporating multidisciplinary collaboration, drawing on expertise from fields such as psychology, sociology, and international relations. This diverse input enriches the process and provides a more holistic understanding of conflict dynamics and potential solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, conflict transformation frameworks offer a comprehensive and sustainable approach to addressing conflicts by focusing on systemic change and the transformation of relationships. This approach sets itself apart by prioritizing long-term peace over short-term gains, seeking to alter hostile dynamics through dialogue, inclusivity, and empowerment. The frameworks emphasize the need for a sophisticated understanding of deep-rooted social and structural issues, advocating for inclusive participation and restorative practices that promote healing.
Despite their potential, implementing conflict transformation frameworks is not without its challenges. These include resistance from entrenched stakeholders, cultural barriers that hinder inclusivity, and the complex, long-term nature of measuring transformation success. However, adopting best practices such as cultural sensitivity, multidisciplinary collaboration, and a commitment to empathy and open dialogue can enhance the effectiveness of these frameworks.
Ultimately, conflict transformation frameworks present a paradigmatic shift in how conflicts are perceived and addressed. They invite stakeholders to view conflicts not just as problems to be resolved but as opportunities for profound societal transformation, ultimately striving to build more peaceful and resilient communities.