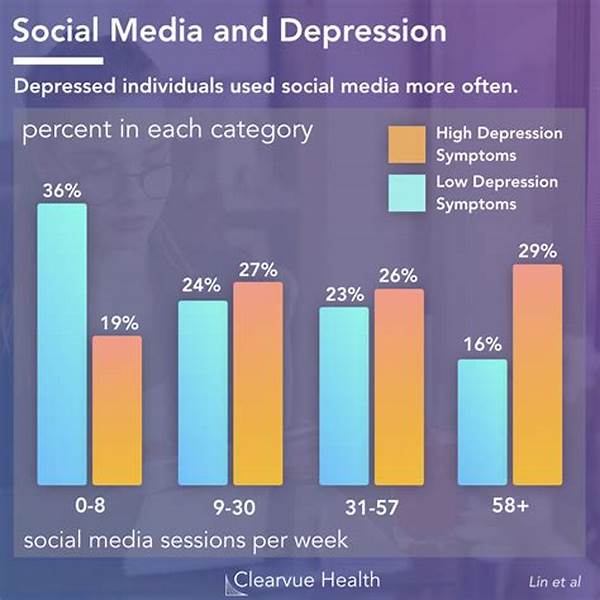
The Correlation between Social Media and Depression
The advent of social media platforms has revolutionized the way individuals communicate and interact globally. However, numerous studies have begun to unveil the potential pitfalls of these digital spaces, particularly concerning mental health. A growing body of research highlights the connection between depression and social media usage, raising concerns among mental health professionals and users alike. This concern stems from various factors, including the tendency of individuals to compare themselves to idealized portrayals of life seen on social media, the prevalence of cyberbullying, and the perpetuation of online negativity. These elements can collectively contribute to feelings of inadequacy, isolation, and, ultimately, depression.
Additionally, excessive social media use can lead to severe disruptions in sleep patterns, which is a known factor contributing to mental health issues, including depression. The constant urge to stay connected and respond to notifications can lead to increased stress and anxiety, detracting from face-to-face social interactions and real-life experiences that are essential for mental well-being. As such, it is imperative to understand the nuances and intricacies of how social media usage can adversely affect mental health, providing a profound yet often overlooked link to depression.
Understanding the Dynamics of Social Media and Mental Health
1. Comparative Analysis: Individuals often engage in unhealthy comparisons on social media, leading to dissatisfaction and depression linked to social media usage.
2. Escalation of Cyberbullying: The anonymity provided by social media can result in cyberbullying, contributing to depression linked to social media usage.
3. Sleep Disruption: Compulsive social media usage can disrupt sleep patterns, further exacerbating depression linked to social media usage.
4. Online Negativity: Negative interactions on social media can create a hostile environment, enhancing the incidence of depression linked to social media usage.
5. Isolation Factor: Although designed for connectivity, social media can create feelings of isolation, paradoxically increasing depression linked to social media usage.
Psychological Impacts of Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms have profoundly changed communication dynamics, but they also present psychological consequences that warrant concern. One of the primary issues associated with these platforms is the amplification of depression linked to social media usage. Many users curate their profiles to reflect an idealized version of themselves, prompting others to engage in constant comparison and self-scrutiny. This phenomenon can significantly diminish self-esteem, contributing to a cycle of negative mental health outcomes such as anxiety and depression.
Moreover, the addictive nature of social media encourages habitual checking and overuse, which detracts from real-world interactions and responsibilities. This compulsive behavior is recognized as a contributor to stress, further establishing the link between depression and social media usage. The need for instant gratification and validation through likes and comments further exacerbates feelings of inadequacy and loneliness. Such factors underline the importance of implementing balanced social media habits to preserve mental health and wellbeing in today’s digital-centric culture.
Further Investigations into Social Media’s Impact
1. Emotional Disturbance: The emotional turbulence resulting from social media confirms the link between depression and social media usage.
2. Social Anxiety: Increased exposure to online scrutiny can heighten social anxiety, aligning with depression linked to social media usage.
3. Perception of Reality: Distorted reality portrayed on social media feeds into depression linked to social media usage.
4. Feedback Loop: The constant feedback mechanism prevalent on social media fosters depression linked to social media usage.
5. Content Overload: A deluge of information can overstimulate users and contribute to depression linked to social media usage.
6. Attention Span Reduction: Social media’s quick content consumption model affects attention span, linked to depression.
7. Emotional Dependency: Users often rely on social media for emotional support, indicative of depression linked to social media usage.
8. Decline in Personal Interactions: Social media diminishes quality of offline interactions, supporting the pattern of depression linked to social media usage.
9. Identity Issues: The struggle to maintain an online identity complicates self-perception, associated with depression.
10. Artificial Interactions: Relationships on social media may lack depth, fostering a connection to depression linked to social media usage.
The Role of Positive Social Media Engagement
Despite the challenges presented, social media can be leveraged positively to support mental health initiatives. Constructive and mindful engagement is crucial to alleviate the negative aspects and foster environments where individuals can share supportive content and resources. By promoting discussions about mental health and encouraging transparency concerning personal challenges, social media platforms can become a source of strength rather than stress.
The emphasis should be placed on facilitating genuine connections and using digital platforms for educational purposes. Implementing digital literacy programs can equip users with skills to navigate the complexities of online interactions responsibly. This approach will help mitigate the prevalence of harmful effects while enhancing the protective nature of social media against depression. Thus, strategic efforts are essential for harnessing the potential of these platforms to assist rather than hinder mental health objectives.
Bridging the Gap: Awareness and Action
Addressing the association between depression linked to social media usage requires comprehensive strategies that encompass both awareness and actionable measures. Educational initiatives targeted towards young users can provide insight into the implications of excessive social interaction through digital means. Establishing clear guidelines and boundaries for social media usage is vital to encourage healthier habits and reduce dependency.
Furthermore, collaboration between mental health professionals and technology developers can pave the way for innovative solutions that prioritize user well-being. By integrating mental health tools and resources within social media platforms, users can be directed towards appropriate support channels. This integrated approach not only promotes awareness but actively contributes to reducing the incidence of depression linked to social media usage, ensuring a healthier digital ecosystem.
Conclusion: Navigating a Digital World
In conclusion, the intricacies of depression linked to social media usage highlight a significant area of concern within modern society. It is evident that while social media platforms serve as powerful communicative tools, their misuse can lead to adverse mental health outcomes. Mindful engagement and conscious consumption of digital content must be reinforced to counteract these effects. The responsibility lies not only with individual users but also with platform creators and mental health advocates to foster a balanced and health-oriented online environment.
Through increased awareness, research, and targeted interventions, the negative impacts of social media can be mitigated, thereby enhancing user experiences and supporting mental well-being. By acknowledging the challenges and taking affirmative action, society can harness the potential of social media for positive change, ensuring it remains a beneficial aspect of everyday life rather than a source of distress.