The increasing interaction between humans and wildlife presents significant challenges that demand urgent attention and comprehensive strategies. Human-wildlife conflict occurs when wildlife requirements overlap with those of human populations, creating adverse impacts on humans or their resources or as a result of humans on wildlife. Understanding and implementing effective human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies is crucial to ensuring the coexistence of humans and wildlife, while protecting both natural ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Understanding Human-Wildlife Conflict
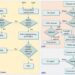
Human-wildlife conflicts are prevalent in areas where expanding human activities encroach upon wildlife habitats. Such conflicts can take various forms, including crop raiding by wildlife, livestock predation, and the transmission of zoonotic diseases. Implementing human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies is pivotal in reducing these adverse impacts and fostering a harmonious coexistence. Strategies can include community-based resource management, the use of technological innovations, and policy interventions that balance human needs with wildlife conservation objectives. By adopting a multidimensional approach, stakeholders can mitigate conflicts, thereby securing livelihoods while safeguarding the biodiversity that underpins vital ecosystem services.
Key Measures in Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation
1. Community Engagement: Empowering local communities to actively participate in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies encourages stewardship and enhances the long-term sustainability of these efforts.
2. Habitat Restoration: Rehabilitating natural habitats reduces encounters between humans and wildlife, serving as a foundational aspect of human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies.
3. Conflict Zoning: Implementing designated zones where human and wildlife activities are spatially separated stands as an effective measure in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies.
4. Early Warning Systems: Deploying technological solutions such as early warning systems is instrumental in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies. This allows timely interventions to prevent potential conflicts.
5. Insurance Schemes: Developing financial mechanisms such as compensation and insurance schemes offers economic resilience to communities, promoting acceptance of human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies.
The Role of Technology in Mitigating Conflicts
Technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies. Drones, GPS tracking collars, and satellite imagery facilitate the monitoring of wildlife movements, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis. By integrating technology, stakeholders can better predict and respond to potential conflicts, reducing the risk to both humans and wildlife. Furthermore, mobile applications tailored to local contexts allow communities to report conflicts promptly and receive expert advice. These technological solutions, when incorporated into broader human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies, significantly contribute to minimizing conflicts.
Legislative and Policy Frameworks
The formulation of comprehensive legislative and policy frameworks is fundamental in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies. Such frameworks should address land-use planning, enforcement of wildlife conservation laws, and transboundary cooperation among governments. Policymakers must align these frameworks with sustainable development goals and integrate considerations for socio-economic contexts. By adopting an inclusive policy approach, the dual objectives of human welfare and wildlife preservation are more attainable, offering a structured pathway to resolving conflicts.
Promoting Coexistence through Education
Education and awareness-raising are instrumental in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies. By fostering an understanding of wildlife behavior and ecological roles, educational initiatives can reduce negative perceptions associated with wildlife. Informational campaigns target different demographics, tailoring messages to both urban and rural settings. Increased awareness encourages tolerance and supports community-based proactive measures. As part of a broader strategy, education empowers individuals to make informed decisions, facilitating peaceful coexistence.
Collaborative Approaches in Conflict Resolution
A collaborative approach involving governments, NGOs, local communities, and international organizations is imperative in human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies. Collaboration ensures that resources and knowledge are shared, enabling the design and implementation of targeted interventions. Stakeholder meetings, workshops, and partnerships facilitate the exchange of best practices and successful case studies. By cultivating a collaborative culture, human-wildlife conflict mitigation efforts are more cohesive, leading to more sustainable outcomes.
Summary and Future Directions
In summary, the implementation of human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies is a complex yet vital endeavor necessitating a multifaceted approach. Prioritizing the creation of comprehensive frameworks that incorporate scientific insights, community needs, and technological innovations is indispensable for effective conflict resolution. By advancing collaborative and inclusive strategies, there is potential to significantly reduce conflicts and foster a sustainable and peaceful coexistence between humans and wildlife.
As human-wildlife conflicts continue to manifest alongside expanding human activities, the demand for robust human-wildlife conflict mitigation strategies will inevitably grow. Future directions should emphasize adaptive management practices, the incorporation of indigenous knowledge systems, and a commitment to conservation that acknowledges human realities. Through persistent efforts and a collective commitment to innovation, the path toward harmonious coexistence remains both hopeful and attainable.