In an era dominated by digital information, the reliability of data sources has become a pivotal concern across all sectors. The integrity and veracity of data constituting the foundation of industries, governments, and academia cannot be overstated. Ensuring the accuracy and dependability of data sources is imperative, as decisions derived from flawed data can lead to significant repercussions. This article explores various aspects of the reliability of data sources, underscoring its importance and the measures required to uphold its standards.
The Importance of Reliability of Data Sources
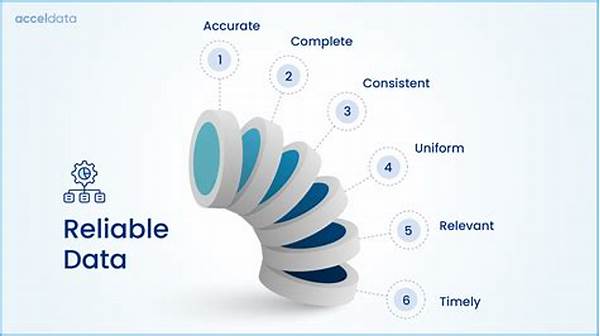
The reliability of data sources is a critical criterion in the assessment of data quality. In research and business environments, the authenticity of the information can influence the outcome of strategic decisions. When data sources lack credibility, it becomes challenging to formulate sound conclusions, which in turn could result in misguided policies or business strategies. Therefore, stakeholders must scrutinize data sources diligently to ensure that they meet stringent reliability criteria. This entails verifying the origin of the data, cross-referencing with other reputable sources, and applying consistent data validation processes. Through these measures, organizations can mitigate risks associated with unreliable data, thus protecting their interests and fostering trust within their operational frameworks.
Methods to Ensure the Reliability of Data Sources
1. Verification: Cross-check data against multiple reputable sources to confirm accuracy and consistency.
2. Validation: Implement quality control processes to assess reliability before using the data.
3. Credibility Assessment: Evaluate the reputation and history of the data provider.
4. Regular Audits: Conduct periodic assessments to ensure ongoing data reliability.
5. Technological Tools: Utilize advanced software tools for data integrity checks.
Challenges in Assessing the Reliability of Data Sources
Evaluating the reliability of data sources involves multifaceted challenges that require careful consideration. One prominent challenge is the identification and evaluation of bias within data. Bias can originate from data collection processes, the subjective interpretation of results, and even technological limitations inherent in certain data-gathering methods. To combat bias, practitioners must employ a rigorous methodological approach, incorporating diverse perspectives to scrutinize data objectively.
Moreover, the sheer volume of digital information poses another significant hurdle in maintaining data reliability. With the exponential growth of data, the ability to systematically validate each piece becomes increasingly strained. Advanced analytical tools and artificial intelligence have commenced playing pivotal roles in supporting data integrity, although these technologies are not without limitations. Ensuring the reliability of data sources calls for a collaborative approach that involves human judgment combined with technological support, both of which need constant evolution to adapt to emerging data complexities.
Factors Impacting the Reliability of Data Sources
The reliability of data sources is shaped by numerous factors. Ensuring data provenance is essential, as understanding the origin helps in assessing its credibility and relevance. Additional factors include:
1. Source Credibility: Reliable data often stems from reputable sources with a history of accuracy.
2. Measurement Precision: Precise measurement methods increase the data’s trustworthiness.
3. Temporal Relevance: Data should be timely to enhance its applicability.
4. Cultural Context: Understanding data within its cultural context aids in its interpretation.
5. Technological Infrastructure: Sophisticated infrastructure can enhance data collection and analysis reliability.
6. Data Governance Policies: Robust policies ensure transparency and accountability.
7. Data Consistency: Uniformity across datasets corroborates the information.
8. User Competency: Skilled analysts proficient in data interpretation bolster reliability.
9. Ethical Considerations: Ethical data use enhances trust and reliability.
10. Transparency and Documentation: Strong documentation provides insight into data collection processes, supporting evaluation.
Enhancing Reliability Through Technological Interventions
In the modern data-driven environment, reliance on technology has become an instrumental strategy in enhancing the reliability of data sources. Tools such as machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence systems enable automatic validation and accuracy checks, significantly reducing the probability of human error. These technologies streamline the process of identifying inconsistencies, thus strengthening the overall integrity of data.
Furthermore, blockchain technology offers innovative solutions for ensuring data immutability, providing a tamper-proof record of data transactions. By implementing decentralized ledgers, organizations can trace the origination and modification of data with heightened transparency. However, the adoption of these technologies should be complemented with robust governance frameworks to ensure responsible management and usage. Therefore, while technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the reliability of data sources, it must be leveraged with caution and responsibility to address potential ethical and legal implications.
Ethical Implications of Data Source Reliability
Reliability of data sources extends beyond technical aspects and delves deeply into ethical territories. Ethical data practice necessitates adherence to principles such as accuracy, fairness, and transparency. The propagation of false or biased information can have adverse societal impacts, reinforcing stereotypes or informing ill-founded decisions that may engender long-term consequences.
Organizations bear the responsibility of cultivating ethical data environments by instituting comprehensive policies and encouraging cultures of integrity among employees. Moreover, there is a growing call for inter-industry collaboration to establish standardized ethical guidelines that guide data sourcing and utilization. Through these concerted efforts, not only is the reliability of data sources enhanced, but also the social trust in organizations’ capacity to handle data responsibly is fortified.
Summary of the Reliability of Data Sources
In conclusion, the reliability of data sources forms the bedrock of informed decision-making across various sectors. Acknowledging the importance of credible data, organizations are tasked with the diligent assessment of their data sources, adopting stringent verification and validation processes to ensure data integrity. Technological advancements such as AI and blockchain play pivotal roles, yet their efficacy remains contingent on responsible governance and ethical practice.
In light of the growing data complexities, fostering a culture of responsibility and transparency is essential in upholding the reliability of data sources. By engaging in ethical practices and leveraging technological innovations responsibly, organizations can enhance trust and make informed decisions that drive positive outcomes. As data continues to shape our future, prioritizing reliability becomes imperative in enabling accurate analysis, sound strategy formulation, and ultimately, societal advancement.