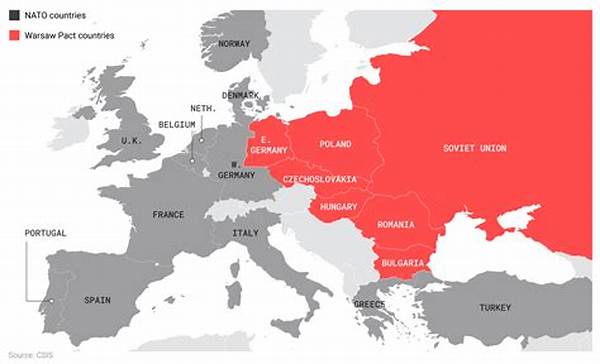
The historical and sociopolitical evolution of Eastern Europe has been significantly shaped by interactions with Western Europe. This influence is deeply embedded within various aspects of Eastern European societies, contributing to transformations in political systems, economies, cultural dynamics, and social structures. The intersection of Western ideologies with the traditional Eastern European framework has been a subject of intense study and discussion, particularly in the post-Cold War era, where integration into Western frameworks accelerated through initiatives like the European Union and NATO membership.
Dynamics of Western Influence in Eastern Europe
The “western influence in Eastern Europe” can be comprehensively observed through changes in governance structures where several countries transitioned from communist regimes to democratic governance. This shift was heavily inspired by Western political ideals and models. Economically, the adoption of free-market principles over previously centralized economic systems marked a significant systemic transformation. Additionally, cultural exchanges have brought about an influx of Western pop culture, media, and educational paradigms, facilitating a blend of cultural and intellectual thought.
The transformation process demanded robust institutional reforms aligned with Western models, which involved embodying transparency, accountability, and rule of law. These changes were complemented by initiatives aimed at bolstering trade relations and fostering economic collaborations, thereby connecting Eastern European markets with broader Western economic frameworks. This socio-economic transformation illustrates the depth of “western influence in Eastern Europe,” where old regimes were reshaped under the weight of Western liberal ideas and practices.
Political and Economic Transformations
1. The shift from centralized governments to democratic systems in Eastern Europe exhibits the profound impact of Western democratic ideals.
2. Economic restructuring in Eastern European nations was largely influenced by free-market economies prevalent in Western Europe.
3. Western influence in Eastern Europe is evident in cultural realms, including music, film, and arts, where Western norms and trends have significantly permeated local culture.
4. Educational reforms aimed to incorporate Western educational philosophies have had a lasting effect on Eastern European academic systems.
5. Western political and economic models have served as a blueprint for institutional reforms throughout Eastern Europe.
Cultural Integration and Hybridization
The deep cultural transformations resultant from Western influence in Eastern Europe are characterized by a complex interplay between traditional Eastern European values and Western lifestyles. This dynamic interaction has led to a hybridization of cultural identities, where traditional practices are interwoven with contemporary Western values. Manifestations of this blend can be observed in the realms of art, fashion, literature, and daily social behaviors, indicating a comprehensive infusion of Western culture.
Moreover, media and technology have played significant roles in this cultural transition. The prevalence of Western television programs, movies, and music, facilitated by the digital era, has gradually shaped cultural tastes and preferences within Eastern European societies. As younger generations grow increasingly attuned to Western modes of expression, there arises an ongoing evolution of cultural identity—one that encapsulates a unique fusion of Eastern and Western elements inspired by “western influence in Eastern Europe.”
Societal Transformations and Challenges
Western influence in Eastern Europe has induced substantial societal shifts, influencing everything from family structures to individual lifestyles. The penetration of Western consumerism has reshaped traditional economic and social habits, changing consumption patterns, lifestyle choices, and the roles within family units. However, this influence is not without its challenges, as tensions arise between the preservation of traditional cultural identities and the adoption of Westernized ways of life.
Furthermore, there are notable discrepancies in the pace of adaptation among different societal segments, resulting in intergenerational divides and socio-economic disparities. While younger demographics tend to favor Western trends, older generations may prefer preserving traditional ways, creating societal rifts. Addressing these complex dynamics requires a nuanced understanding of both the benefits and drawbacks associated with “western influence in Eastern Europe.”
Education and Intellectual Exchange
The educational landscape in Eastern Europe has embraced various Western pedagogical approaches and reforms. The Bologna Process exemplifies this influence, aimed at harmonizing higher education systems across Europe, including Eastern European nations. This transformation has facilitated academic mobility and held the promise of broader career prospects for students from this region, underlining the educational aspect of “western influence in Eastern Europe.”
Such changes have fostered heightened collaboration between Eastern and Western academic institutions, resulting in enriched research opportunities and extended networks. However, aligning with Western academic standards has necessitated significant systemic changes, including updating curricula, adopting new teaching methodologies, and enhancing institutional governance, reflective of the tangible education exchange driven by Western influence.
Summary of Western Influence in Eastern Europe
In summary, the “western influence in Eastern Europe” is a multifaceted phenomenon affecting diverse domains, including political landscapes, economic structures, cultural identity, societal norms, and educational systems. This impact, although profound and pervasive, is characterized by varying degrees of reception and adaptation across different Eastern European societies. While embracing democratic values, free-market economies, and cultural diversity vividly indicates Western influence, the region continues to grapple with maintaining its historical and cultural uniqueness.
As Eastern European nations further integrate into global frameworks, the challenge remains to balance innovation and tradition, ensuring that the adoption of Western models does not completely overshadow indigenous heritage. The ongoing dialogue between Eastern and Western paradigms promises continued evolution, where cooperative exchanges foster mutual understanding and respect, further illustrating the lasting legacy of “western influence in Eastern Europe.”