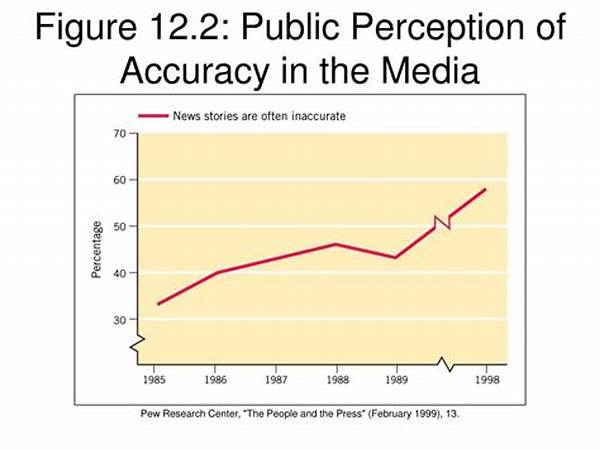
The Interconnection between Public Perception and Media Coverage
In contemporary society, the interplay between public perception and media coverage has become a pivotal area of interest. The media, as a conduit of information, wields substantial influence over public perception, shaping opinions and attitudes across a wide array of issues. This dynamic relationship dictates not only what information is disseminated to the public but also how it is framed and interpreted. Media coverage serves as the primary source through which individuals form perceptions about current events, public figures, and social issues. Consequently, it plays a critical role in setting public agendas and priorities. Moreover, the evolution of digital media has amplified this influence, allowing for rapid and widespread dissemination of information, thus intensifying the impact on public perception. As such, it becomes imperative to scrutinize the mechanisms through which media coverage can sway public opinion and the ethical responsibilities that accompany this power. Understanding the nuances of this relationship can provide insights into the societal implications of media practices and their consequences on public discourse and democracy.
The Role of Media in Shaping Public Perception
1. Media coverage is pivotal in shaping public perception by determining which stories receive attention and how they are presented, thus influencing the public’s understanding and interpretation of events.
2. Through selective reporting, media coverage can highlight specific issues, thereby prioritizing public perception towards particular societal concerns, while potentially omitting others.
3. The tone and framing used in media coverage significantly impact public perception, as it can evoke specific emotions and reactions, thereby shaping the viewers’ attitudes and beliefs.
4. Public perception is affected by the repetition of messages in media coverage, where continuous exposure reinforces certain viewpoints, making them more prevalent in the public’s consciousness.
5. Media coverage’s influence on public perception is evident in the creation of stereotypes and narratives that affect societal attitudes, highlighting the importance of responsible journalism.
Effects of Bias in Media Coverage on Public Perception
The occurrence of bias in media coverage has profound implications on public perception. Bias manifests in various forms, such as partisan reporting, selective story inclusion, and misleading headlines. When media outlets show favoritism, it compromises the objectivity and integrity of the information presented, leading to skewed public perception. This selective reporting fosters a fragmented understanding of issues, as individuals receive information filtered through particular lenses. Consequently, it can perpetuate polarization within society by dividing public opinion along ideological lines. Media coverage that fails to present balanced viewpoints can also lead to misinformation, thereby impairing the public’s ability to make informed decisions. Addressing media bias is crucial to ensure that public perception is based on factual, balanced, and comprehensive reporting. It is the responsibility of media institutions to uphold ethical standards in journalism, recognizing the significant influence they have on shaping public discourse. Acknowledging and correcting bias in media coverage can foster a more informed and united public, ultimately strengthening democratic processes and societal cohesion.
Factors Influencing Public Perception and Media Coverage
1. Media Ownership: Ownership patterns influence media coverage, potentially leading to biases that shape public perception according to the interests of owners.
2. Political Context: The political climate can affect media coverage, with outlets aligning perceptions with prevailing political ideologies to resonate with their audience.
3. Technology: Advancements in technology have transformed media coverage, impacting public perception through the prevalence of digital and social media platforms.
4. Social Bias: Cultural and social biases within media coverage can influence public perception by reinforcing stereotypes and social norms.
5. Economic Interests: Media coverage may be swayed by commercial interests, affecting how information is presented and perceived by the public.
6. Sensationalism: Sensationalist reporting in media coverage can skew public perception by exaggerating details to attract viewers, often at the expense of accuracy.
7. Credibility: The credibility of media outlets affects public perception, as sources perceived as reliable are more likely to shape opinions.
8. Framing: The framing of news stories in media coverage can direct public perception by emphasizing specific elements over others.
9. Gatekeeping: The process of selecting which stories receive coverage influences public perception by highlighting certain events over others.
10. Audience Engagement: Interactions between media and its audience can shape public perception by reflecting societal interests and concerns in coverage.
Ethical Implications of Media Coverage on Public Perception
In the modern information era, ethical considerations take center stage in discussions about media coverage and its impact on public perception. The media holds significant power to influence opinions, attitudes, and societal norms, raising concerns about the ethical responsibilities of media organizations. One major ethical implication is the perpetuation of misinformation or biased reporting, which can manipulate public perception and erode trust in media institutions. Ensuring accuracy, fairness, and objectivity in reporting is crucial to maintaining public trust and upholding democratic values. Furthermore, the ethical conundrum of prioritizing sensationalism over substance challenges the integrity of media coverage. As stories are chosen and framed for maximum impact, there is a risk of distorting public perception to align with dramatic narratives rather than factual reporting. It is imperative for media outlets to balance the necessity of attracting audiences with upholding ethical standards that promote an informed and engaged public.
Understanding the ethical implications of media coverage requires an ongoing commitment to transparency and accountability. Journalists and media organizations must actively engage in ethical decision-making processes to ensure that public perception is constructed on a foundation of truth and fairness. By advocating for ethical journalism, media can contribute to a more informed society, fostering dialogue that bridges divides and encourages collective understanding. The role of the media as a guardian of public interest is one that carries immense responsibility, necessitating a conscientious approach to coverage that respects the power it holds in shaping public perception.
Media Influence on Public Opinion and Social Behavior
The influence of media coverage on public perception extends beyond mere opinion formation, affecting social behavior and cultural norms. As a primary source of information, media coverage holds the power to shape societal attitudes and drive social change. The portrayal of issues, events, and individuals in the media can set the tone for public discourse, influencing how society reacts to and engages with various phenomena. Through its coverage, the media can bring attention to pressing social issues, mobilizing public perception towards advocacy and reform. The impact of media coverage on social behavior is evident in areas such as health communication, where public perception can drive awareness and preventative actions in response to health crises.
Moreover, media’s role in reflecting and shaping cultural norms underscores its ability to influence social behavior. As cultural trends are highlighted in media coverage, they contribute to the shifting narratives that define public perception of what is acceptable or desirable. The media’s framing of gender roles, for example, can perpetuate stereotypes or challenge societal perceptions, ultimately influencing behavior. As such, the implications for media coverage in shaping social behavior are profound, necessitating a careful and ethical approach to reporting. By understanding the reverberations of media influence on public perception and social behavior, media institutions can contribute positively to societal evolution, promoting a culture of awareness, inclusivity, and progressive change.
Summary: The Dynamic Interplay between Public Perception and Media Coverage
In summary, the intricate relationship between public perception and media coverage represents a defining feature of modern society. Media coverage acts as the lens through which individuals interpret the world, influencing opinions, attitudes, and behaviors. The power wielded by media institutions in shaping public perception is immense, underscoring the critical role of responsible journalism. As media coverage sets agendas, highlights societal priorities, and frames issues, it directly influences the public’s understanding and engagement with the world around them. This relationship is further complicated by factors such as media ownership, political context, and technological advancements, each contributing to the way media shapes public perception.
The ethical implications of media influence on public perception cannot be overstated. Misinformation and biased reporting can distort public perception, eroding trust in media and democratic institutions. However, ethical journalism that prioritizes accuracy, fairness, and inclusivity can foster informed citizenry and promote social progress. Understanding this dynamic interplay requires ongoing dialogue and self-regulation within media institutions, ensuring that public perception is guided by reliable and balanced coverage. In navigating this landscape, the media must recognize its responsibility as a steward of information, with the capacity to both reflect and shape the society it serves. Acknowledging the power of media coverage is essential in fortifying the foundations of informed public discourse and advancing societal cohesion.