Introduction to Biodiversity Loss in Conflict Areas
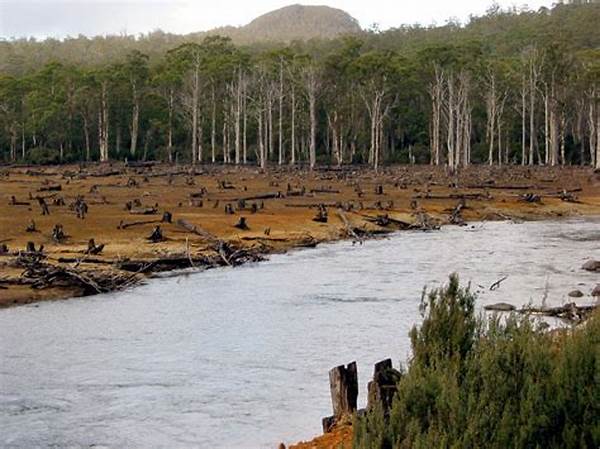
Biodiversity loss in conflict areas is an alarming consequence often overshadowed by immediate human suffering and geopolitical considerations. These regions, caught in the throes of war and unrest, witness significant environmental degradation that disrupts ecosystems, threatening both flora and fauna. The constant human encroachment, combined with the sheer brutality of armed conflicts, results in rampant deforestation, destruction of natural habitats, and a decline in biological diversity. These detrimental effects contribute to an alarming reduction in the ecological richness that these areas once boasted. Despite these challenges, the global community must evaluate and address the hidden costs of war, ensuring that post-conflict recovery efforts include a focus on restoring and protecting the biodiversity that has been lost.
Drivers of Biodiversity Loss in Conflict Areas
Armed conflicts bring about destructive activities such as logging, mining, and agricultural encroachment, leading to biodiversity loss in conflict areas. The need for resources such as timber and minerals during wars accelerates habitat destruction. Furthermore, landmines and explosives pose persistent threats to wildlife by contaminating habitats and hindering ecosystem recovery.
Failing governance in conflict zones undermines conservation efforts, leaving natural reserves vulnerable to exploitation. The absence of effective regulations results in unabated poaching and illegal wildlife trade. Lack of law enforcement encourages unsustainable practices among communities struggling for survival.
The displacement of human populations induces pressure on natural resources, causing biodiversity loss in conflict areas. Refugee influxes necessitate the exploitation of local resources for shelter, fuel, and food, further straining already fragile ecosystems. This new demographic reality intensifies wildlife conflicts, leading to a vicious cycle of resource scarcity.
Military activities have a significant impact on natural landscapes, contributing to biodiversity loss in conflict areas. The establishment of military bases in ecologically sensitive zones interrupts wildlife corridors, affecting species’ migration patterns. Additionally, the use of chemical weapons contaminates soil and water, thereby threatening indigenous species.
Resource scarcity fueled by armed conflicts exacerbates the risk of biodiversity loss in conflict areas. With depleted resources, communities often resort to unsustainable practices like slash-and-burn agriculture. The degradation of vegetation cover diminishes the habitats necessary for the survival of various species, reducing biodiversity.
Consequences of Biodiversity Loss in Conflict Areas
The consequences of biodiversity loss in conflict areas are far-reaching and extend beyond environmental degradation. One significant impact is the loss of ecosystem services that are crucial for human survival. These services include water purification, climate regulation, and soil fertility. The degradation of these ecosystem functions due to biodiversity loss can exacerbate poverty and food insecurity in affected regions, creating a cycle of hardship.
Additionally, biodiversity loss in conflict areas poses a significant threat to global biodiversity as a whole. Many conflict zones are located in biodiversity hotspots, regions that are home to a vast array of endemic species. The destruction of these habitats can lead to the extinction of rare and endangered species, contributing to a decrease in global biodiversity. Conservation efforts, therefore, must be prioritized even amid conflict to prevent irreversible losses to our planet’s biological heritage.
Strategies for Mitigating Biodiversity Loss in Conflict Areas
To combat biodiversity loss in conflict areas, various strategies must be implemented. Firstly, international collaboration is essential to address root causes by supporting sustainable development and peace-building. By fostering diplomatic relations, nations can work towards implementing effective conservation policies that prioritize ecological protection amidst conflict.
Establishing transboundary conservation areas can help mitigate biodiversity loss in conflict areas by facilitating cooperation between neighboring countries. These areas allow shared management of natural resources, vital for maintaining ecological continuity. The cross-border approach also empowers local communities to participate in conserving their biological heritage.
Capacity building among local populations is crucial in mitigating biodiversity loss in conflict areas. By providing education and training on sustainable resource management practices, communities can adopt alternative livelihood strategies that do not harm the environment. Empowered communities play an active role in preserving their biodiversity.
Partnerships with NGOs and financial institutions can help fund and support conservation projects in biodiversity loss-prone conflict areas. The involvement of external stakeholders provides essential resources and technical expertise for developing effective conservation initiatives. These partnerships strengthen local resilience towards biodiversity threats.
Embedded monitoring and evaluation systems are pivotal in assessing the efficacy of conservation efforts in conflict areas. These systems provide valuable data on ecological changes, helping researchers identify trends, threats, and successes. Reliable information forms the basis for adaptive management strategies to effectively address biodiversity loss.
Importance of International Cooperation in Addressing Biodiversity Loss
International cooperation is vital in tackling biodiversity loss in conflict areas. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and international agencies can lead to effective policy formulation and resource allocation. Joining forces allows for the pooling of expertise and knowledge, ensuring comprehensive strategies to mitigate biodiversity loss.
Shared responsibilities and commitments in addressing biodiversity loss in conflict areas help to bridge gaps in local capacities. Global entities can provide technical assistance, funding, and political support for conservation programs. Such collaboration ensures that efforts are adequately resourced and align with international conservation goals.
Promoting the exchange of information and best practices among countries facing similar challenges is essential in addressing biodiversity loss in conflict areas. By learning from one another, stakeholders can adopt effective strategies and avoid past pitfalls. Knowledge sharing ensures adaptable and context-specific approaches to conservation.
International agreements provide a platform for holding participating countries accountable for enforcing conservation efforts. These frameworks push governments to prioritize biodiversity protection, even amid conflict. The normative pressure from international agreements encourages nations to adopt sustainable practices and deter environmentally harmful activities.
International cooperation encourages long-term commitment to biodiversity conservation in conflict areas. It entices countries to embed conservation within their national agendas, ensuring continuous efforts beyond immediate crises. Sustaining attention on biodiversity preservation helps maintain global ecological balance and resilience.
The Role of Local Communities in Preventing Biodiversity Loss
Local communities play a pivotal role in preventing biodiversity loss in conflict areas. Engaging community members in conservation efforts fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards protecting their environments. Their indigenous knowledge and proximity to natural resources make them invaluable stewards of biodiversity.
Empowering local communities through participatory conservation programs enhances their capacity to manage resources sustainably in conflict areas. By involving community members in decision-making processes, conservation initiatives become more culturally relevant and effective. Participatory approaches ensure that community needs align with biodiversity goals.
Community-led conservation practices can mitigate biodiversity loss in conflict areas by promoting sustainable resource management. Traditional practices, such as agroforestry and rotational farming, minimize environmental impacts while supporting livelihoods. These sustainable methods balance human needs with ecosystem preservation.
Local community involvement in biodiversity conservation fosters resilience and adaptation in conflict areas. Communities are better equipped to respond to environmental challenges by relying on their knowledge and practices. Resilient communities contribute to the stability and protection of biodiversity in conflict-prone regions.
Strengthening community networks and collaborations with NGOs and governments enhances their ability to prevent biodiversity loss in conflict areas. Access to resources, technical expertise, and advocacy support enables communities to address threats effectively. These collaborations empower communities to champion enduring conservation efforts.
Summary of Biodiversity Loss in Conflict Areas
In conclusion, biodiversity loss in conflict areas is an urgent issue demanding immediate attention and action. Armed conflicts directly impact natural ecosystems, leading to habitat destruction, resource depletion, and the destabilization of ecological balances. As such, there is an imminent need for comprehensive strategies that address this multifaceted problem, integrating ecological considerations into peace-building efforts.
Effective solutions to biodiversity loss in conflict areas require a collaborative approach involving international, national, and local stakeholders. By fostering partnerships, sharing resources, and building capacity, the global community can work towards restoring ecological integrity in conflict zones. Additionally, empowering local communities to take the forefront in conservation initiatives will ensure sustainable and culturally relevant outcomes. The preservation of biodiversity amidst conflicts safeguards not only environmental health but also the socio-economic well-being of affected populations, paving the way for a more resilient future.