The phenomenon of ecosystem disruption due to militarization is a burgeoning concern that has garnered attention from environmentalists, policymakers, and scholars alike. This topic is not merely a matter of ecological disturbance but also involves complex political, social, and economic dimensions. Militarization, characterized by the expansion of armed forces and their impact on natural landscapes, disrupts various ecological systems, leading to irreversible environmental damage. This article seeks to unravel the multifaceted impact of militarization on ecosystems and underscores the urgent need for sustainable conflict resolution strategies that harmonize with environmental preservation.
The Ecological Impact of Militarization
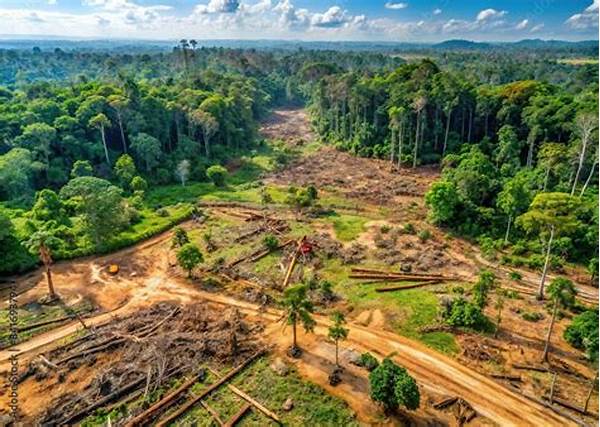
Ecosystem disruption due to militarization manifests in various forms, significantly affecting biodiversity and natural habitats. The construction of military bases, the deployment of weaponry, and combat exercises in pristine environments often lead to deforestation, habitat loss, and pollution. Numerous studies have documented instances where military activities have severely compromised the ecological balance, driving several species to the brink of extinction. The long-term consequences of such activities not only pose a threat to biodiversity but also affect local communities that rely on these ecosystems for their livelihoods. The exacerbation of these environmental challenges demands immediate attention and action from both military and environmental stakeholders.
Furthermore, the noise pollution from military exercises and the use of heavy machinery contribute to a hostile environment for wildlife. This ecosystem disruption due to militarization often results in the migration of species, disrupting food chains and altering the ecological equilibrium. Additionally, residual wastes and chemicals from military operations pose a potential hazard to both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, compelling a re-evaluation of military strategies that neglect environmental conservation. Addressing these ecological concerns is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the health of both natural and human communities in affected regions.
Strategies for Mitigating Ecological Damage
1. The implementation of stringent environmental regulations is vital to minimizing ecosystem disruption due to militarization. These regulations should mandate environmental impact assessments prior to any military activity in ecologically sensitive areas.
2. Investment in eco-friendly technology within military operations can substantially reduce the negative effects of ecosystem disruption due to militarization. Incorporating sustainable practices can mitigate environmental harm while maintaining military readiness.
3. Restoration programs aimed at rehabilitating environments affected by ecosystem disruption due to militarization should be prioritized. These programs can help in restoring biodiversity and maintaining ecological integrity.
4. Encouraging dialogue and collaboration between military forces and environmental agencies is crucial for addressing the challenges of ecosystem disruption due to militarization. Such partnerships can foster innovative solutions that balance security needs with environmental conservation.
5. Raising awareness about the consequences of ecosystem disruption due to militarization is essential. Educational initiatives can inform policymakers and the public about the importance of protecting natural habitats from militarization’s detrimental effects.
Socioeconomic Consequences of Militarization
The ecosystem disruption due to militarization extends beyond environmental degradation, affecting the socioeconomic dynamics of local communities. In many regions, these disruptions result in the displacement of populations, loss of livelihoods, and social unrest. Communities dependent on fishing, agriculture, and forestry are particularly vulnerable, as militarization often leads to restricted access to vital resources. This displacement not only impacts the local economy but also contributes to broader sociopolitical instability. Addressing these socioeconomic repercussions necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates community needs with environmental restoration efforts.
Moreover, the financial resources allocated to militarization could instead be directed towards sustainable development initiatives, offering long-term economic benefits while preserving ecological balance. By re-assessing budgetary priorities, governments can foster economic resilience in affected regions and create opportunities for community-led conservation projects. This shift in focus from militarization to sustainability is imperative for achieving a harmonious coexistence between human activity and nature. It is therefore crucial for international bodies to advocate for policies that align national security objectives with ecological and community well-being.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation plays a pivotal role in mitigating the effects of ecosystem disruption due to militarization. Collaborative efforts among nations can lead to the development of comprehensive policies that prioritize environmental security alongside national defense. Establishing international frameworks for monitoring and regulating military activities in ecologically vulnerable regions is fundamental to ensuring global ecological stability. By sharing best practices and coordinating efforts, countries can effectively address the transboundary challenges posed by militarization.
Furthermore, international treaties focused on environmental protection can incentivize nations to adopt eco-friendly military strategies. Such agreements can facilitate the exchange of knowledge and technology, fostering innovation in environmentally sustainable defense practices. The success of these initiatives depends on the willingness of nations to commit to cooperative endeavors that transcend geopolitical interests. Ultimately, international collaboration is essential for creating a global paradigm that values ecological preservation as an integral component of security strategies.
Environmental Ethics and Militarization
The ethical considerations surrounding ecosystem disruption due to militarization call for a reevaluation of current military practices. Ethical frameworks that emphasize stewardship of the environment advocate for the responsible use of natural resources and the protection of wildlife. These principles challenge militaristic approaches that prioritize immediate strategic gains over long-term ecological consequences. By integrating ethical considerations into military decision-making processes, nations can develop strategies that respect ecological boundaries and prioritize sustainable development.
Additionally, fostering a culture of environmental ethics within military organizations is crucial for effecting meaningful change. Training programs that emphasize the importance of ecological preservation can cultivate a deeper understanding of the environmental impact of military activities among personnel. This shift in organizational culture is essential for fostering a commitment to environmentally responsible practices and ensuring the long-term viability of natural ecosystems.
Conclusion
In summary, the ecosystem disruption due to militarization presents a multifaceted challenge that demands immediate and sustained attention. The environmental, socioeconomic, and ethical dimensions of this issue underscore the need for comprehensive strategies that balance military objectives with ecological preservation. By prioritizing sustainable practices, investing in eco-friendly technology, and fostering international cooperation, nations can mitigate the detrimental effects of militarization on ecosystems. Furthermore, embracing ethical considerations and engaging affected communities are critical components of a holistic approach to resolving this pressing concern. Ultimately, the path to sustainable security requires a reimagining of traditional militaristic paradigms to encompass the preservation of our planet’s ecological integrity.