The Evolution of Global Military Alliances
In the evolving landscape of international relations, global military alliances have played a pivotal role in maintaining world order and addressing various challenges. Over the decades, these alliances have evolved to adapt to the dynamic geopolitical environment. While their primary objective remains collective defense and security, alliances have expanded their roles to include crisis management, peacekeeping, and the promotion of democratic values. Global military alliances in recent history have had significant implications on national policies, defense strategies, and global peace.
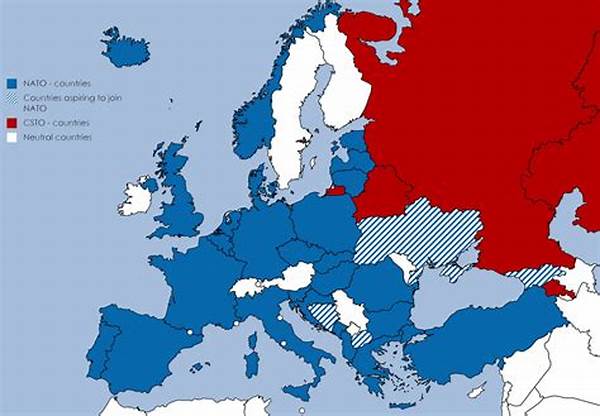
One notable example of a military alliance is the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), established in 1949, which has undergone numerous transformations in response to the shifting political climate. As the Cold War ended, NATO shifted its focus towards out-of-area operations, crisis response, and partnerships with non-member countries. Similarly, alliances such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation and broader coalition efforts in regions like the Middle East reflect the complex and multifaceted nature of global military alliances in recent history.
As we dissect these global military alliances, it becomes evident that they are not static. The pressures of modern-day threats such as terrorism, cyber warfare, and regional conflicts demand agile and responsive alliance structures. Nations continue to band together under these alliances, reinforcing the importance of collective security and sustained collaboration. Understanding the role of global military alliances in recent history requires examining their impact on peacekeeping, geopolitical stability, and fostering international cooperation.
Key Aspects of Recent Military Alliances
1. Global military alliances in recent history emphasized adaptability to new threats, such as cyber warfare and terrorism. These alliances have had to evolve beyond conventional military engagements to address multifaceted global security challenges effectively.
2. The proliferation of nuclear weapons influenced the formation and strategies of global military alliances in recent history. Deterrence remains a crucial component, with alliances striving to prevent nuclear escalation while promoting arms control and disarmament initiatives.
3. Recent conflicts have highlighted the importance of joint operations and interoperability among member nations. Global military alliances in recent history have invested heavily in training and exercises to enhance collaboration and readiness.
4. The role of non-state actors in conflicts has necessitated a re-evaluation of traditional military strategies. Global military alliances in recent history have increasingly focused on intelligence sharing, counterterrorism, and counterinsurgency operations.
5. Economic and political considerations often guide the decision-making processes within these alliances. Global military alliances in recent history have witnessed debates on burden-sharing, illustrating the complexities involved in sustaining collective defense initiatives.
Dynamics of Alliance Formation
The intricacies of alliance formation and sustainment bear significant importance in understanding global military alliances in recent history. At their core, alliances represent commitments between nations to pool resources, similarly aligned interests, and counteract potential threats. The decision-making process in forming alliances typically involves negotiations where political, economic, and military dynamics intermingle to establish terms that benefit all parties involved.
For instance, alliances like NATO began primarily as a mechanism of defense against the Soviet bloc during the Cold War. However, they evolved beyond their initial purposes, embodying broader security and political commitments. Changes in political leadership, economic conditions, and evolving threats such as terrorism have continuously reshaped these alliances. Moreover, the inclusion of new member states has broadened an alliance’s scope, as seen with NATO’s expansion.
Analyzing global military alliances in recent history also highlights the importance of trust, reliability, and shared values among member nations. Trust fosters an environment where nations feel secure in relying on mutual aid, while shared values ensure ideological and political harmony. Consequently, the effectiveness of an alliance is often contingent upon these elements, emphasizing their critical role in the success of these international agreements.
Implications and Challenges
Global military alliances in recent history have significantly impacted international relations, shaping the global balance of power. Such alliances have influenced not only defense strategies but have had extensive political and economic ramifications. The strategic partnerships formed within alliances provide a platform for dialogue and cooperation, serving as a deterrent to potential aggressors while reinforcing global security.
However, these alliances are not without challenges. One persistent issue is the complexity of coordinating among diverse member states with varying national interests and defense capabilities. Achieving consensus on matters of strategic importance can often be a protracted process, necessitating diplomatic negotiations and compromise. Additionally, global military alliances in recent history have faced criticism regarding equitable burden-sharing, with debates often arising over the distribution of responsibilities among member nations.
Another issue confronting these alliances is evolving security threats. As the nature of warfare transforms with technological advancements, such as cyber threats, alliances must adapt to ensure preparedness and resilience. This requires continual investment in defense infrastructure, joint training exercises, and developing new operational doctrines that address contemporary challenges. Hence, the adaptive capacity of global military alliances in recent history remains pivotal to their efficacy and longevity.
Strategic and Political Landscape
Reflecting on the strategic and political landscape, global military alliances in recent history destabilize some regions while fostering stability in others. Alliances form strategic buffers and create a balance of power, preventing dominance by a single nation or coalition. This balance inherently upholds a degree of peace and deters major conflicts, thereby influencing global geopolitical dynamics.
Moreover, alliances also act as conduits for political dialogue. Through such platforms, member nations can engage with each other, forging diplomatic ties and resolving differences within a framework encouraging peace. The diplomatic engagement engendered by these bodies plays a crucial role in assuaging tensions and mediating conflicts that might otherwise lead to military confrontations.
However, alliances are prone to internal and external pressures. Internal pressures often emanate from economic, political, and strategic interests among member nations, which may vary over time or due to leadership changes. Externally, geopolitical shifts, such as the rise of new powers, demand strategic recalibrations within these alliances. Thus, to maintain relevance, the architecture of global military alliances in recent history requires continuous evaluation and adjustments.
The Future Trajectory of Alliances
Looking ahead, the trajectory of global military alliances in recent history will likely be influenced by emerging technological innovations, shifting power paradigms, and evolving security threats. With the world becoming increasingly interconnected, alliances must embrace a proactive approach, fostering resilience against diverse challenges ranging from cyber threats to climate change.
The reliance on global military alliances as a security apparatus indicates the pressing need for these entities to engage in comprehensive reforms and capacity-building initiatives. Such endeavors would not only enhance their collective defense mechanism but also fortify their ability to undertake peacekeeping and humanitarian missions globally. Ultimately, the evolution of these alliances is contingent upon their agility and willingness to adapt to a rapidly changing world.
Furthermore, alliances will continue to play a role in fostering international cooperation, bridging diplomatic divides, and promoting stability. As nations navigate the complexities of globalization and technological proliferation, global military alliances in recent history stand as essential frameworks for ensuring sustained peace and security. Their continued relevance depends on the ability to address contemporary challenges while maintaining the foundational tenets that have historically defined these partnerships.
Summary
In retrospect, global military alliances in recent history have been instrumental in shaping international defense and security strategies. They have provided member nations with frameworks for collective security, helping to mitigate threats and deter potential adversaries. These alliances, while complex, embody a commitment to maintaining global stability and peace, facilitating cooperation, and fostering diplomatic dialogue.
As we examine the landscape of these alliances, it is evident that they are not static institutions. Continuous evolution is necessary to address emerging challenges and adapt to changing geopolitical dynamics. Global military alliances in recent history underscore the intricate balance of power, the necessity for political cooperation, and the importance of shared values. These elements underpin their effectiveness and enduring significance in international relations.
The future of these alliances will hinge on their capacity to innovate, embrace multifaceted roles, and engage with the broader international community. The complexities of modern threats mandate that alliances transcend traditional military paradigms, leveraging technology and fostering resilience to navigate uncertainties. As the international arena continues to evolve, global military alliances in recent history remain pivotal to ensuring global peace and security.