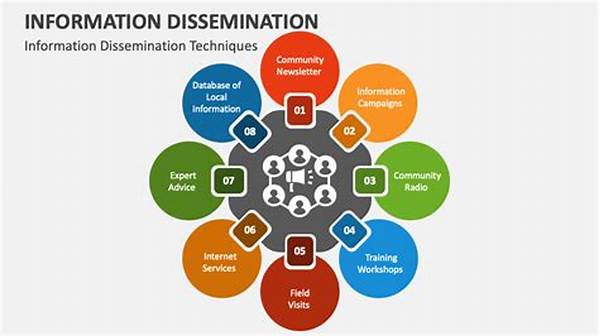
In the contemporary global landscape, conflicts have evolved to encompass not only military engagements but also a complex interplay of information dissemination. The role of information dissemination during conflicts has become increasingly significant, influencing both public perception and the strategic outcomes of the conflicts themselves. The methodologies and channels through which information is shared can significantly affect the course and resolution of conflicts. This article explores the multifaceted nature of information dissemination during conflicts, examining its various dimensions and implications.
Communication Strategies in Conflict Situations
The adoption of effective communication strategies is crucial during conflicts to ensure that information dissemination is accurate and timely. During conflicts, information dissemination plays a vital role in shaping the narrative and influencing public opinion. Governments, media outlets, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) often engage in the dissemination of information to maintain transparency and credibility. However, the rise of misinformation and disinformation poses significant challenges to these efforts.
In the realm of conflicts, accurate information dissemination is paramount to countering false narratives and ensuring that the public remains informed. Communication strategies employed may include press releases, social media, and official government briefings. The goal is to provide clear, factual, and unbiased information to the public and stakeholders involved. Furthermore, information dissemination during conflicts should prioritize ethical considerations to avoid exacerbating tensions.
Additionally, technological advancements have transformed how information is disseminated during conflicts. With the proliferation of digital platforms, information can be rapidly shared globally. This immediacy enhances the potential for both positive and negative impacts on conflict resolution. Stakeholders must therefore be adept at managing information dissemination to support peace-building efforts and mitigate harm.
Challenges in Information Dissemination during Conflicts
1. Information Reliability: Ensuring the reliability of information dissemination during conflicts is challenging due to the prevalence of misinformation and deliberate disinformation campaigns aiming to manipulate public perception.
2. Technological Barriers: Information dissemination during conflicts can be hindered by technological barriers, such as limited internet access in conflict zones, which restricts the flow of accurate information.
3. Cultural Sensitivity: Effective information dissemination during conflicts requires cultural sensitivity and understanding to ensure that messages are appropriately framed and communicated.
4. Security Risks: The dissemination of information during conflicts carries inherent security risks, as sensitive information can be exploited by adversaries to gain strategic advantages.
5. Resource Constraints: Resource limitations often impede the ability of agencies to effectively manage information dissemination during conflicts, affecting the reach and accuracy of their messages.
The Role of Media in Information Dissemination during Conflicts
The media plays a pivotal role in the process of information dissemination during conflicts. As both a source and a channel, media organizations bear the responsibility of providing balanced and accurate news coverage. They act as intermediaries, bridging the gap between official sources and the general public. The impact of media on public perception can be profound, influencing opinions and potentially affecting policy decisions and conflict resolutions.
During conflicts, impartiality and accuracy should be central to media reporting. Journalistic integrity and ethical standards must guide information dissemination to avoid inflaming tensions. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on combatting misinformation, a task that requires media outlets to verify sources and corroborate information before publication. The role of international media in covering conflicts also highlights the need for cross-cultural understanding and comprehensive reporting.
Moreover, media organizations must navigate the rapid pace of information dissemination during conflicts. With real-time updates and social media platforms, the speed at which information is shared has increased dramatically. This necessitates quick yet thorough reporting to ensure that information is accurate and responsibly communicated.
Technological Innovations in Information Dissemination during Conflicts
1. Digital Platforms: Digital platforms facilitate real-time information dissemination during conflicts, allowing stakeholders to disseminate updates quickly and efficiently.
2. Data Analytics: The use of data analytics in information dissemination during conflicts enables the filtering and prioritization of critical information to aid decision-making processes.
3. Social Media: Social media serves as a powerful tool for information dissemination during conflicts, offering opportunities for rapid sharing and engagement with global audiences.
4. Mobile Communication: Mobile technology enhances information dissemination during conflicts by providing individuals in conflict zones with access to vital information through mobile networks.
5. Satellite Imagery: satellite imagery is pivotal for reliable information dissemination during conflicts by providing visual evidence and supporting transparency efforts.
6. Cyber Security: Cybersecurity measures are crucial for safeguarding the integrity of information dissemination during conflicts and protecting against cyber threats.
7. Artificial Intelligence: The integration of AI technologies in information dissemination during conflicts assists in processing large volumes of data to extract relevant insights.
8. Open Source Intelligence: The practice of open-source intelligence enables the collection and analysis of publicly available information for effective dissemination during conflicts.
9. Virtual Reality: Virtual reality technologies offer innovative opportunities for immersive information dissemination during conflicts, enhancing understanding and empathy.
10. Secure Communication Channels: Secure communication channels are essential for protecting sensitive information dissemination during conflicts and ensuring confidentiality.
Ethical Considerations in Information Dissemination during Conflicts
The ethical considerations surrounding information dissemination during conflicts are of paramount importance. It is imperative that all entities engaging in the dissemination of information adhere to principles of truthfulness, transparency, and accountability. Misrepresentation or manipulation of information can exacerbate existing conflicts and pose severe ethical dilemmas.
Organizations must be especially vigilant in maintaining ethical standards to ensure that their information dissemination efforts do not contribute to harm or perpetuate conflict. This includes a commitment to fact-checking, the avoidance of sensationalism, and the protection of vulnerable populations. Ethical conduct demands that information dissemination during conflicts strives to support humanitarian aid, peace-building efforts, and conflict resolution.
Additionally, consideration must be given to the privacy and security of those involved in or impacted by conflict. Responsible information dissemination requires the safeguarding of personal information and the prevention of its misuse. Efforts to ensure ethical conduct in information dissemination during conflicts are integral to upholding human dignity and fostering trust among affected communities.
The Impact of Social Media on Information Dissemination during Conflicts
Social media has transformed the landscape of information dissemination during conflicts. Platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram act as conduits for instantaneous information sharing, allowing individuals and organizations to communicate effectively with diverse global audiences. The democratization of information dissemination via social media encourages dialogue and fosters connection across geographical boundaries.
However, the pervasive nature of social media also introduces complexities. The rapid spread of misinformation on these platforms can disrupt information dissemination during conflicts and pose significant challenges to the establishment of factual narratives. Efforts to combat this issue involve implementing mechanisms for verification and moderation, as well as advocating for digital literacy among users.
In addition to its challenges, social media’s impact on information dissemination during conflicts offers numerous opportunities. It enables the amplification of marginalized voices and provides a platform for eyewitness reports and on-ground updates, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of conflict dynamics. Ultimately, social media plays a dual role, functioning as both a powerful tool for connection and communication and a potential catalyst for misinformation.
Conclusion: Information Dissemination during Conflicts
In conclusion, information dissemination during conflicts is a complex and dynamic process that requires careful consideration of strategic, ethical, and technological factors. The interplay between media, technology, and communication strategies underscores the significance of responsible and accurate information dissemination during conflicts. The implications of such dissemination efforts extend beyond the immediate scope of conflict, influencing public perception and contributing to long-term resolution and peace-building initiatives.
Stakeholders engaged in the process of information dissemination during conflicts must navigate a rapidly evolving landscape, taking into account the challenges and opportunities presented by modern technologies and media channels. By prioritizing truthfulness, cultural sensitivity, and ethical conduct, they can mitigate harm and promote transparency and understanding. The role of information dissemination during conflicts, therefore, extends beyond its immediate context and plays a critical role in fostering dialogue, accountability, and the potential for lasting peace.