In today’s digital age, the overwhelming abundance of information available at our fingertips necessitates a robust framework for evaluating the credibility of various sources. As information consumers, distinguishing between legitimate and dubious sources is pivotal to forming accurate and reliable understandings of the world. The following sections will delve into various aspects, methodologies, and significance of information source credibility assessment, providing a comprehensive guide on navigating the vast sea of information with discernment.
Understanding the Concept of Information Source Credibility Assessment
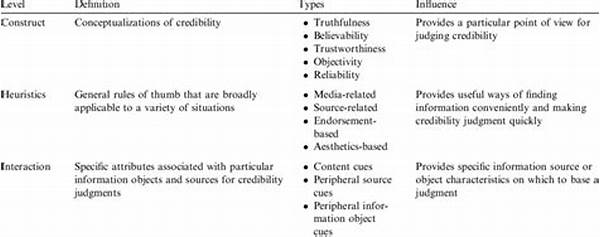
Information source credibility assessment is a critical component in evaluating the reliability and validity of information disseminated through various channels. The process involves scrutinizing the authenticity of the source, its expertise, and the relevance of the information provided. In an era where misinformation is rampant, mastering this assessment skill is indispensable for anyone seeking to make informed decisions based on accurate data.
A credible information source is typically characterized by authority and trustworthiness. Authority pertains to the source’s expertise and the recognition it receives within its respective field. Meanwhile, trustworthiness involves the source’s track record in presenting reliable and unbiased information. The task of credibility assessment is thus twofold: determining the level of expertise and the historical consistency in accuracy. While traditional media outlets were primarily the gatekeepers of information in the past, the rise of the internet and social media has democratized information dissemination, making the ability to assess source credibility more crucial than ever.
To elevate one’s proficiency in information source credibility assessment, individuals are advised to cultivate a critical mindset, consistently analyzing and cross-referencing information to ensure its reliability. This process is not solely an academic exercise but a practical necessity in a world inundated with excessive data. By integrating credibility assessment into everyday information consumption practices, one can effectively navigate the complexities and challenges inherent in the digital information landscape.
Key Elements of Information Source Credibility Assessment
1. Authority of the Source: Evaluating an information source’s authority involves checking the credentials and expertise of the author or organization. Information source credibility assessment starts with ensuring that the source has recognized authority in the relevant field.
2. Objectivity and Bias: It is essential to consider any potential biases or agendas. Information source credibility assessment involves identifying whether a source presents information objectively or if it skews facts to fit a particular narrative.
3. Accuracy of Information: Cross-reference the information with other credible sources to confirm its accuracy. In information source credibility assessment, fact-checking is crucial to ascertain the reliability of the data presented.
4. Currency and Relevance: Assessing the timeliness and relevance of the information helps ensure that it suits the current context. Part of information source credibility assessment is verifying that the information is up-to-date and pertinent.
5. Source Transparency: Understanding the source’s funding and affiliations contributes to a more informed assessment. Full disclosure of potential conflicts of interest is a significant aspect of information source credibility assessment.
The Impact of Information Source Credibility Assessment on Society
The rapid dissemination of information has revolutionized how society functions, affecting everything from personal decision-making to global geopolitical dynamics. Information source credibility assessment plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the information guiding these decisions is precise and trustworthy. In a world susceptible to misinformation, individuals armed with effective credibility assessment skills contribute to fostering a more informed public.
Quality assessments of information sources have profound implications for democratic processes. When citizens are equipped with accurate information, they can engage more meaningfully in civic activities, such as voting and community advocacy. The role of information source credibility assessment is thus essential in nurturing informed citizenry, capable of discerning fact from fiction in political discourse and media representations.
Furthermore, the economic sphere is not immune to the influence of information credibility. Business decisions often hinge on data and analyses from presumably credible sources. Ensuring these sources are trustworthy mitigates risks associated with investments and strategic planning. Thus, the ability to perform an effective information source credibility assessment transcends individual benefit, fostering broader economic stability and innovation.
Methods to Enhance Information Source Credibility Assessment Skills
Information source credibility assessment is an evolving skill that benefits from constant refinement and practice. The following strategies offer guidance on improving proficiency:
1. Critical Thinking Development: Cultivate an analytical mindset that questions the validity of information and its sources.
2. Media Literacy Education: Participate in media literacy programs aimed at enhancing skills in assessing the credibility of diverse information formats.
3. Cross-Referencing Techniques: Utilize various sources to verify facts and ensure consistency in the information presented.
4. Digital Literacy Programs: Engage in courses that teach effective navigation of digital environments and the identification of credible online resources.
5. Bias Recognition Training: Become adept at detecting bias, understanding how it affects information presentation and decision-making processes.
6. Research Methodologies: Familiarize oneself with robust research methods and how they contribute to authoritative information.
7. Verification Tools: Employ digital tools and platforms specifically designed for fact-checking and source verification.
8. Peer Review Processes: Understand the importance of peer-reviewed sources in academic and professional settings.
9. Transparency Evaluation: Develop skills in assessing the transparency of sources, including funding and potential conflicts of interest.
10. Ongoing Education: Commit to lifelong learning in information evaluation, keeping abreast of emerging trends and challenges in the information landscape.
The Role of Technology in Information Source Credibility Assessment
Advancements in technology have greatly influenced the process of information source credibility assessment. Artificial intelligence and machine learning, for instance, offer sophisticated tools for verifying facts and identifying credible sources. These technologies can analyze vast volumes of data at unprecedented speeds, assisting users in discerning the reliability of information.
The integration of AI-driven solutions into credibility assessment practices represents a significant shift. Algorithms can determine the authenticity of images, videos, and news content, thereby enhancing the accuracy of information judgments. Moreover, technology facilitates the creation of databases that offer comprehensive information on the backgrounds and histories of various sources, further supporting credibility assessment efforts.
Despite these technological advances, human engagement and critical reasoning remain indispensable in the information source credibility assessment process. While technology can aid in initial evaluations, the nuanced understanding of context and intention often requires human interpretation. Thus, an optimal approach combines technological tools with human judgment, ensuring a thorough and reliable assessment of information sources.
Challenges Facing Information Source Credibility Assessment
Despite the clear methods and technologies available, numerous challenges persist in the realm of information source credibility assessment. The volume and speed of information dissemination complicate the ability to thoroughly assess sources before consuming information. This rapid pace can overwhelm even the most experienced evaluators, necessitating continuous advancements in assessment methodologies.
A significant challenge lies in the pervasive nature of digital misinformation, often designed to appear credible. These sources exploit cognitive biases and technological limitations to spread falsehoods. Consequently, individuals must remain vigilant and continuously educate themselves about new tactics employed by purveyors of misinformation.
Additionally, cultural and contextual differences can affect how information is interpreted and assessed. What is considered credible in one cultural setting may not hold the same weight in another, leading to potential misunderstandings and misinterpretations. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that includes education, technological innovation, and cross-cultural understanding to advance the science and practice of information source credibility assessment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, information source credibility assessment remains an essential skill in navigating the complexities of modern information landscapes. By understanding the key elements, methods, and challenges involved in this process, individuals are better equipped to discern reliable information from misleading data. The role of technology, coupled with human critical thinking, offers a promising pathway to enhancing accuracy in information assessments.
The implications of these practices extend far beyond individual benefits, influencing societal, economic, and political spheres. A society that values and practices effective information source credibility assessment fosters informed citizens, sound decision-making, and robust democratic processes. Ultimately, the commitment to ongoing education and adaptation ensures resilience and accuracy in an ever-evolving information environment.