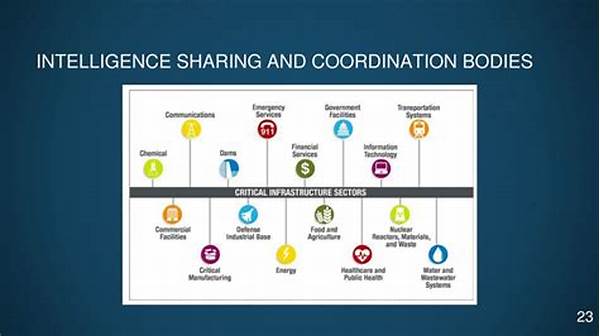
Importance of Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
Intelligence sharing and coordination are pivotal components in ensuring national and international security. In an era marked by complex global threats, seamless synergy among agencies is paramount. By collaborating effectively, intelligence agencies can pool their resources and expertise to counteract threats more efficiently. This collaboration is not merely an operational enhancement but a strategic necessity. Intelligence sharing and coordination facilitate the dissemination of critical information, enabling timely responses to crises. By working together, nations can leverage each other’s strengths, addressing vulnerabilities that no single entity could manage independently. As threats transcend borders, the importance of effective intelligence sharing becomes increasingly apparent. Organizations must adopt robust systems that ensure the accuracy, confidentiality, and prompt exchange of information to maintain global security.
Intelligence sharing and coordination also promote transparency and trust among nations. By actively engaging in shared intelligence exercises, countries can foster diplomatic relationships, building a network of allies committed to mutual security goals. This reciprocal exchange acts as a foundation for a unified approach to combating terrorism, cyber threats, and other international challenges. Furthermore, coordinated intelligence efforts contribute to the optimization of resources. Agencies can avoid duplicating efforts and reduce operational redundancies, ensuring that intelligence operations are both efficient and effective. This optimization not only saves time and money but also enables a more agile response to emerging threats.
Challenges in Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
1. One significant challenge in intelligence sharing and coordination is ensuring data privacy and security. Agencies must implement stringent safeguards to protect sensitive information while maintaining open communication channels.
2. Different organizational cultures and protocols may hinder effective intelligence sharing and coordination. Harmonizing these differences requires strategic alignment and mutual understanding among the participating entities.
3. Trust is a foundational element in intelligence sharing and coordination. Building and maintaining trust among international partners can be difficult, yet it is essential for successful collaboration.
4. Technological disparities between agencies can impede intelligence sharing and coordination. Standardized platforms and technologies are necessary to facilitate seamless information exchange.
5. Legal and regulatory constraints present challenges to intelligence sharing and coordination. Navigating these complexities requires careful consideration and alignment with international laws and agreements.
Strategies for Enhancing Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
To bolster intelligence sharing and coordination, agencies must first commit to establishing robust communication channels. These channels must be secure, efficient, and capable of handling a diverse range of data types. Investing in cutting-edge technology is imperative to ensure that all parties involved are on an equal footing, reducing technological discrepancies that could hinder effective communication. Regular inter-agency meetings and task forces can play a pivotal role in strengthening cooperation and ensuring that intelligence sharing is both accurate and timely. Furthermore, developing standardized protocols that transcend individual agency peculiarities can drastically enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Moreover, fostering an environment of trust and mutual respect is vital in intelligence sharing and coordination. Agencies must prioritize transparency and cultivate confidence among international partners, assuring them of the confidentiality and integrity of shared information. By building strong bilateral and multilateral relationships, stakeholders can work collectively to identify and mitigate potential threats. Simultaneously, there must be a concerted effort to harmonize legal and regulatory practices, ensuring that intelligence sharing and coordination remain within the bounds of legitimate international frameworks. This harmonization not only facilitates smoother operations but also reinforces the legality and ethical standards expected of global intelligence collaboration.
Benefits of Effective Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
1. Intelligence sharing and coordination enhance global security by providing comprehensive threat assessments and timely responses.
2. Collaborative intelligence operations optimize resource utilization, preventing unnecessary duplication of efforts and ensuring cost efficiency.
3. Effective intelligence sharing and coordination bolster alliances, fortifying diplomatic relationships through mutual security commitments.
4. Timely and accurate intelligence dissemination aids in preemptive threat neutralization, safeguarding national and international interests.
5. By facilitating cross-border collaboration, intelligence sharing and coordination drive innovation in threat detection and analysis technologies.
6. Strategic intelligence sharing enables a unified response to global challenges, fostering international stability and peace.
7. Coordination in intelligence efforts mitigates misunderstandings and miscommunications, enhancing operational coherence.
8. Shared intelligence databases promote broader access to critical information, empowering agencies with comprehensive situational awareness.
9. Enhanced cooperation through intelligence sharing streamlines decision-making processes, enabling decisive and informed actions.
10. Intelligence sharing and coordination build a network of trusted partners, enhancing collective resilience against emerging threats.
Historical Context of Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
Throughout history, intelligence sharing and coordination have played a critical role in shaping geopolitical landscapes. During significant global conflicts, such as the World Wars, intelligence-sharing alliances were formed to thwart adversarial advances. This historical precedence underscores the timeless nature of intelligence cooperation. As the nature of warfare has shifted towards asymmetrical threats in the 21st century, the methodologies of intelligence sharing and coordination have evolved. Today, advanced technology facilitates instantaneous information exchanges, enabling real-time responses to dynamic situations. The successes and challenges of past intelligence operations offer valuable lessons for contemporary global security strategies.
The advent of globalization and technological advancements has further necessitated the need for intelligence sharing and coordination. The interconnectivity of economic systems, communication networks, and travel has increased the complexity of modern-day threats. Terrorism, cybercrime, and international espionage are no longer isolated issues; they require a concerted effort from the global community. As such, intelligence sharing and coordination have become indispensable tools in safeguarding civilizations from multifaceted threats. By examining the historical trajectory of intelligence collaboration, stakeholders can chart a progressive course towards more effective and efficient outcomes.
Technological Impact on Intelligence Sharing and Coordination
The integration of technology into intelligence sharing and coordination has revolutionized the manner in which agencies operate. Digital platforms allow for the rapid dissemination of information across geographical boundaries, ensuring that all relevant parties have access to the latest intelligence. Advanced data analytics tools enable the transformation of raw data into actionable insights, enhancing decision-making processes and operational strategies. Machine learning and artificial intelligence have further augmented traditional intelligence methodologies, providing predictive capabilities and identifying patterns that may elude human analysts.
However, the reliance on technology also presents new challenges for intelligence sharing and coordination. Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks, emphasizing the necessity for robust protective measures to safeguard sensitive information. Additionally, the digital divide among nations can exacerbate disparities in intelligence capabilities, making it crucial to prioritize technological cooperation and capacity-building initiatives. The evolving technological landscape demands a constant reassessment of intelligence sharing practices, ensuring that they remain aligned with the highest standards of efficiency, security, and ethical responsibility.
Summary and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, intelligence sharing and coordination are indispensable elements in the modern security architecture. As global threats continue to evolve, the importance of cooperative intelligence efforts has never been more apparent. By fostering an environment of trust and collaboration, agencies can enhance their collective security capabilities, addressing challenges that transcend national borders. The integration of technology and the harmonization of legal practices stand as critical components in advancing intelligence sharing efforts, ensuring that they remain adaptive to the changing dynamics of global security.
Looking forward, the future of intelligence sharing and coordination will likely be shaped by emerging technologies and global geopolitical shifts. As such, it is essential for nations to remain agile and proactive, continuously evaluating and refining their intelligence strategies. By embracing innovation and maintaining an unwavering commitment to collective security, the international community can better prepare for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Through sustained efforts in intelligence sharing and coordination, global peace and stability can be pursued with renewed vigor and determination, providing a safer and more secure world for future generations.