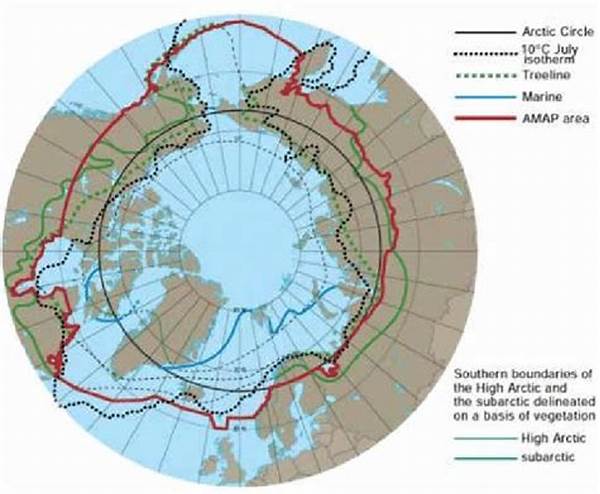
The Arctic region, characterized by its harsh climate and delicate ecosystems, has garnered significant geopolitical interest in recent years. This interest is driven by the potential abundance of natural resources and new shipping routes that have become more accessible due to climate change. Therefore, monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries has become a crucial task for nations with vested interests in the region. The delineation and surveillance of these boundaries ensure peaceful coexistence and equitable resource sharing among the nations involved.
Technological Advancements in Boundary Monitoring
In the realm of monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries, technological advancements have played an indispensable role. Remote sensing technology, such as satellites equipped with synthetic aperture radar, has enhanced the precision with which territorial demarcations can be assessed. These technologies provide critical data in real-time, allowing for swift responses to potential boundary disputes. Moreover, advancements in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology enable detailed, low-altitude observations that complement satellite data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the ever-changing Arctic landscape.
The evolution in data analytics has further transformed the process of monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries. Sophisticated algorithms process vast amounts of data to detect subtle shifts in ice formations and territorial elements, which may indicate encroachments or natural shifts that require diplomatic attention. These technological innovations have not only facilitated more accurate boundary monitoring but also contributed to international collaboration in the management of the Arctic region.
Legal Frameworks Governing the Arctic
Effective monitoring of Arctic territorial boundaries necessitates a robust legal framework. International agreements, including the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), serve as the foundation for resolving disputes and ensuring compliance with agreed boundaries. These legal instruments provide a standardized set of rules for the demarcation and utilization of resources within the Arctic.
National sovereignty and international cooperation are harmonized through these legal agreements, thus ensuring that monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries aligns with global governance protocols. Countries are obliged to respect each other’s territories, and any disputes are resolved through diplomatic channels rather than force. Such frameworks are essential in maintaining peace and stability in a region of shared interest.
The Role of Environmental Considerations
As monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries advances, environmental considerations have become increasingly significant. The Arctic ecosystem is remarkably fragile; thus, any exploitative activities must be balanced with ecological preservation. Continuous monitoring supports this balance by providing data on environmental impacts resulting from territorial activities.
Environmental non-governmental organizations (ENGOs) play a pivotal role in advocating for rigorous monitoring of the Arctic environment in tandem with territorial boundaries. These organizations raise awareness about the potential adverse effects of unchecked resource extraction and emphasize the need for sustainable practices. Thus, monitoring efforts not only address territorial integrity but also underscore the importance of safeguarding the Arctic’s environmental health.
Economic Implications of Boundary Monitoring
The economic implications of monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries are profound. The Arctic holds vast untapped reservoirs of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, making it a focal point for economic expansion. Accurate boundary monitoring ensures equitable resource distribution and prevents conflicts that could disrupt global supply chains.
Effective monitoring further supports new economic opportunities such as Arctic tourism and shipping. Tourism operators rely on clear territorial delineations to establish safe and legal routes for visitors, while shipping companies depend on established boundaries to navigate new routes that reduce travel time and costs. Thus, comprehensive boundary monitoring underpins economic growth in the Arctic while averting disputes.
Challenges in Monitoring Arctic Boundaries
Despite technological and legal advancements, challenges persist in monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries. The remoteness of the region and extreme weather conditions pose logistical challenges that can impede surveillance efforts. Moreover, shifting ice patterns due to climate change introduce uncertainties that complicate boundary delineation.
Geopolitical tensions further exacerbate these challenges. Competing national interests can lead to disputes over boundary interpretations, requiring diplomatic engagement and international cooperation to resolve. Consequently, continuous investment in technology, along with robust diplomatic initiatives, is essential to surmount these challenges and ensure effective boundary monitoring in the Arctic.
Diplomatic Efforts to Enhance Boundary Monitoring
Diplomatic efforts are critical in enhancing the monitoring of Arctic territorial boundaries. International forums, such as the Arctic Council, provide platforms for dialogue and cooperation among Arctic states. These forums facilitate the exchange of technological expertise, promote joint research initiatives, and enhance mutual understanding of boundary-related issues.
Bilateral and multilateral agreements strengthen collaboration by establishing joint monitoring systems and shared databases. These cooperative frameworks foster transparency and trust among nations, reducing the potential for conflict and ensuring the stability of Arctic territorial boundaries for future generations.
Summary of Arctic Boundary Monitoring
In conclusion, monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries is a multifaceted endeavor that requires concerted efforts across technological, legal, environmental, economic, and diplomatic dimensions. The integration of advanced technology with legal and environmental considerations provides a robust mechanism for maintaining territorial integrity. Despite challenges such as harsh environments and geopolitical tensions, ongoing diplomatic engagement and international collaboration are imperative for effective boundary monitoring.
The Arctic holds immense potential for economic growth, and safeguarding its territorial boundaries ensures that resources are utilized responsibly and equitably. As climate change continues to reshape the region, constant vigilance in monitoring Arctic territorial boundaries will remain crucial in preserving peace, promoting sustainable development, and protecting the Arctic’s unique ecosystem for future generations.