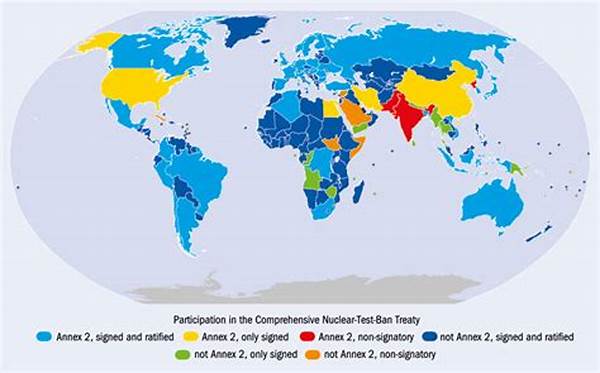
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) remains a pivotal element in global disarmament and non-proliferation efforts. Despite its significance, the ratification of the CTBT has been met with varied responses from countries around the world. The process of ratifying the treaty involves intricate legal and diplomatic steps, reflecting each country’s stance on nuclear weapons. The ratification of the CTBT signifies a country’s commitment to ceasing the testing of nuclear weapons, thus upholding international peace and stability.
Pathway to Ratification
The journey towards the ratification of the CTBT is characterized by complex negotiations and policy considerations. Although the treaty was opened for signature in 1996, its entry into force is contingent upon the ratification by 44 specific nuclear-capable states. As of now, several of these countries have yet to ratify the treaty, posing challenges to its full implementation. The ratification process involves each state examining the treaty’s implications for their national security and regional dynamics. While many countries have embraced the treaty, others remain hesitant, citing security concerns and geopolitical tensions. The ratification of the CTBT remains an essential step for a safer, nuclear-weapons-free world.
Significance of the Ratification of CTBT Treaty
1. The ratification of the CTBT treaty is crucial for reinforcing the global non-proliferation regime.
2. It symbolizes international consensus on the cessation of nuclear weapons testing.
3. Ratification strengthens global security by mitigating the risks associated with nuclear testing.
4. It serves as a confidence-building measure among nations, promoting transparency and trust.
5. The ratification of the CTBT treaty is a testament to a nation’s commitment to multilateral diplomacy and peace.
Challenges in Achieving Full Ratification
Achieving the complete ratification of the CTBT presents numerous challenges. Political, strategic, and technical hurdles continue to impede progress in some regions. Nations still possessing reservations about ratification often cite the need to maintain a credible nuclear deterrent. Furthermore, verification measures, while robust, are subject to scrutiny and debate. This hesitance underscores the need for international dialogue and cooperation to address the concerns of these states. Ultimately, the ratification of the CTBT by all required parties is essential to usher in an era of comprehensive nuclear disarmament. Cooperation and mutual assurance are vital to overcoming the barriers that have stalled the treaty’s full ratification.
Implications of Non-Ratification
The failure to achieve universal ratification of the CTBT holds significant implications for international security. Without its full implementation, the treaty’s potential to prevent nuclear proliferation and testing is severely undermined. This inaction poses risks not only to regional stability but also to global peace. Non-ratification compromises the trust and confidence necessary for effective arms control and disarmament efforts. Consequently, continued advocacy and diplomatic engagement are imperative. The international community must persist in its efforts to achieve the ratification of the CTBT to deter the revival of nuclear testing practices. A coordinated global approach remains indispensable for realizing this goal.
The Role of Civil Society
Civil society plays a crucial role in advancing the ratification of the CTBT. Non-governmental organizations, academic institutions, and advocacy groups work tirelessly to promote awareness and understanding of the treaty’s importance. By engaging in public discourse, these entities amplify the call for comprehensive ratification. They lobby governments, influence public opinion, and collaborate with international bodies to foster a climate conducive to ratification. Their efforts highlight the treaty’s significance not only for governments but for humanity as a whole. Through education and advocacy, civil society can facilitate the necessary political will to bring the CTBT into force.
Regional Dynamics and Ratification
Regional dynamics play a pivotal role in the ratification of the CTBT. Geo-political tensions influence a country’s decision to ratify, often leading to strategic calculations and security concerns. In regions where historical rivalries exist, ratification may be perceived as a vulnerability, impeding progress. Despite these challenges, regional cooperation frameworks can help build consensus. Confidence-building measures and multilateral dialogues serve as platforms to address mutual security concerns, paving the way for ratification. Regional organizations and alliances must actively engage in promoting the treaty to underscore its benefits for collective security and stability.
Summary and the Way Forward
In summary, the ratification of the CTBT remains an imperative step towards achieving global nuclear disarmament. Its ratification is critical in deterring nuclear proliferation and promoting international security. Although the pathway to full ratification is fraught with challenges, sustained dialogue and cooperation are essential. The international community, along with civil society, must continue to advocate for the treaty’s implementation, emphasizing its role in preventing nuclear testing. Successful ratification demands a concerted effort from all nations to transcend regional conflicts and prioritize collective security. As we look to the future, it is clear that the global community must remain steadfast in its commitment to achieving the ratification of the CTBT, ensuring a safer and more secure world for future generations.