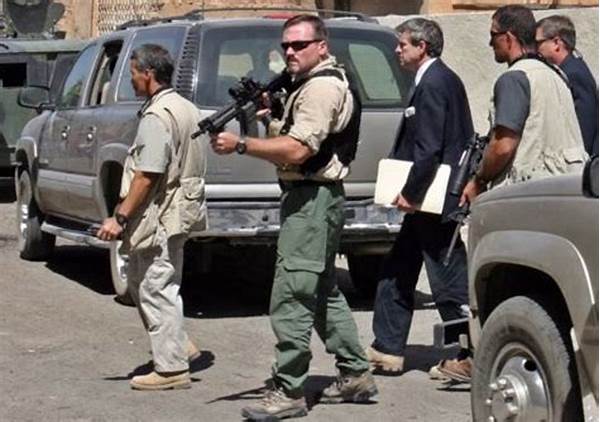
Evolution of Private Military Contractors
The rise of private contractors in international military operations has become a defining characteristic of contemporary warfare. This trend has been propelled by the changing nature of global conflicts, characterized by an increased reliance on technological prowess and specialized knowledge that private entities provide. Governments, faced with budget constraints and operational demands, find private military companies (PMCs) to be a flexible alternative to traditional military forces. Such contractors offer a wide array of services, including logistics, security, intelligence, and operational support, significantly impacting the dynamics of international military engagements. Furthermore, PMCs bring efficiency and expertise, yet their involvement also raises ethical and legal concerns, such as accountability and the potential for conflict of interest. As the dependency on these contractors intensifies, it invites a re-evaluation of international laws and military ethics to better integrate these entities into the framework of global peace and security.
Motivations Behind Outsourcing to Private Contractors
The rise of private contractors in international military operations is driven by several factors:
1. Financial Efficiency: Governments can cut costs by outsourcing instead of deploying national armed forces.
2. Expertise Accessibility: PMCs offer highly specialized skills not readily available within national militaries.
3. Flexibility and Rapid Deployment: Private contractors can be mobilized quickly and operate in diverse environments.
4. Political Considerations: Outsourcing minimizes public scrutiny and political fallout associated with military interventions.
5. Resource Allocation: States can focus military resources on strategic operations while PMCs handle auxiliary tasks.
Implications for International Military Conduct
The rise of private contractors in international military operations has significant implications for global military conduct. The blending of private and public forces introduces complexity into oversight and accountability mechanisms. As these contractors play increasingly central roles in operations, questions about their adherence to international laws and codes of conduct have emerged. Critics argue that PMCs, prioritized for profit, might sidestep regulations that bind regular military forces. Conversely, proponents highlight their proficiency and adaptability in complex conflict zones. Yet, the integration of private contractors into military strategy calls for robust international regulatory frameworks, ensuring their operations align with established ethical standards. The ongoing discourse around their roles underscores a pressing need for consensus on policy and practice regarding the rise of private contractors in international military operations.
Challenges and Concerns Involving PMCs
1. Legal Ambiguities: The rise of private contractors in international military operations often occurs in a gray area of international law.
2. Accountability Issues: Monitoring and enforcing accountability remains a challenge given their non-state actor status.
3. Ethical Dilemmas: Their operations can provoke ethical dilemmas, including the use of force and treatment of civilians.
4. Diplomatic Implications: The presence of PMCs can complicate diplomatic relations between states.
5. Cultural Sensitivity: Contractors must navigate complex cultural landscapes, risking potential friction.
6. Standardization Gaps: Variations in operational standards can affect collaboration with national forces.
7. Security Risks: Overreliance on PMCs may undermine national security apparatus.
8. Dependence Risk: Increasing reliance may weaken state military capabilities.
9. Legitimacy Concerns: The use of PMCs can erode perceived legitimacy of military interventions.
10. Sustainable Peacebuilding: PMCs influence long-term peace and stability outcomes in conflict zones.
Strategic Integration of Private Contractors
The rise of private contractors in international military operations necessitates strategic integration to optimize their strengths while mitigating risks. Given their growing prominence, it is crucial that these entities are effectively incorporated into formal military strategies. Policymakers must establish clear guidelines and comprehensive oversight frameworks to ensure coordination between private and national forces. Ensuring transparency and accountability in operations is fundamental to maintaining international law compliance. Additionally, ongoing dialogue between governments, PMCs, and international bodies is essential for establishing norms and standards. As PMCs are poised to remain indispensable to future military operations, developing mechanisms that promote ethical conduct and operational efficiency becomes imperative. Ultimately, the strategic integration of private contractors must reinforce, rather than undermine, the objectives of global peace and security amid their continued rise in international military operations.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Needs
The rise of private contractors in international military operations underscores a pressing need for robust legal frameworks and regulatory oversight. Current international regulations often fall short in addressing the complex roles and responsibilities these contractors assume. While numerous international treaties articulate principles of conduct for state militaries, similar binding frameworks for PMCs are lacking, creating gaps in accountability. Addressing these limitations requires international cooperation to develop comprehensive legal instruments that establish clear standards for PMC operations. Moreover, effective regulatory mechanisms must encompass monitoring, reporting, and enforcing compliance to uphold ethical standards. Establishing certification and licensing protocols can also ensure uniformity across contractors. In parallel, ongoing assessments of the PMC industry are crucial to adapt regulatory measures in response to evolving operational contexts. Through rigorous legal and regulatory approaches, the rise of private contractors in international military operations can align with the broader aspirations of global peace and security.
Summary and Future Considerations
In summary, the rise of private contractors in international military operations represents a paradigmatic shift in modern warfare. This evolution reflects a deeper trend towards the privatization of military functions, driven by the need for specialized skills and cost-effective solutions. While PMCs provide undeniable advantages in enhancing military capacity and capability, their integration raises questions of legal accountability, ethical conduct, and state sovereignty. Developing cohesive regulatory frameworks and fostering transparency are imperative to managing the complexities PMCs introduce. As their roles expand, it is vital for stakeholders to engage in sustained dialogue and collaboration, ensuring that these entities not only enhance operational results but also adhere to international norms. Looking ahead, the rise of private contractors in international military operations will continue to shape military policies and strategies, necessitating ongoing scrutiny and adaptation to safeguard the principles and objectives of global security.