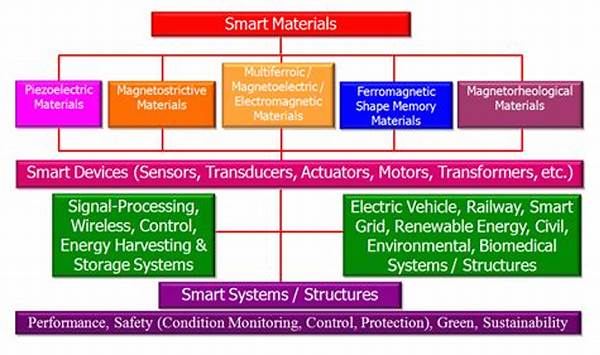
In the rapidly evolving domain of defense technology, the emergence of smart materials has ushered in a new era of innovation and capability. Smart materials possess the ability to respond dynamically to external stimuli, thereby revolutionizing their application in military settings. These materials, which include shape-memory alloys, piezoelectric materials, and electroactive polymers, offer unprecedented advantages in terms of adaptability, efficiency, and resilience. As nations seek to bolster their defense systems in the face of evolving threats, smart materials for defense applications have become a focal point of research and development. Their potential to enhance military effectiveness cannot be overstated.
The Rise of Smart Materials in Modern Warfare
The integration of smart materials into defense applications marks a significant milestone in modern warfare. The primary appeal of these materials lies in their adaptability and multifunctionality. For instance, shape-memory alloys can change shape in response to temperature changes, offering capabilities like morphing aircraft wings. Similarly, piezoelectric materials produce an electric charge in response to mechanical stress, which can be harnessed in sensors for precise monitoring of equipment health. Electroactive polymers, on the other hand, can change size or shape when stimulated, enabling innovative uses in robotics and actuators. The unique characteristics of smart materials for defense applications are critical in creating more resilient and adaptive systems, allowing for advanced defensive measures and proactive threat response.
Applications and Implications in Military Equipment
1. Adaptive Camouflage Technology: Smart materials for defense applications have led to the development of adaptive camouflage systems capable of changing colors to blend with various environments, enhancing stealth operations.
2. Self-Healing Materials: These materials automatically repair damages, maintaining structural integrity and extending the lifespan of military vehicles and equipment.
3. Structural Health Monitoring: Sensors made from smart materials provide real-time data on the condition of infrastructure and vehicles, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing safety.
4. Energy Harvesting: Piezoelectric materials convert mechanical movements into energy, providing sustainable power solutions for soldiers and unmanned systems.
5. Robotics and Actuators: The use of electroactive polymers in smart materials for defense applications enhances robotic autonomy and efficiency, allowing for advanced maneuverability in complex terrains.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementation
While the potential of smart materials for defense applications is immense, several challenges must be addressed to fully integrate these materials into military systems. One prominent issue is the high cost associated with research and manufacturing, which can be a significant barrier for widespread adoption. Furthermore, the durability and reliability of smart materials under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments, need to be thoroughly tested to ensure efficacy in real-world scenarios. On the other hand, the opportunities are vast; the innovation pipeline continues to grow as research and technology advance, driving down costs and enhancing material performance. Collaborations between defense agencies, academic institutions, and private sectors are pivotal in tackling these challenges and unlocking the potential of smart materials for defense applications.
Future Prospects and Strategic Developments
The future of defense technology hinges significantly on the advancements in smart materials. As research progresses, these materials are expected to become more cost-effective and easier to produce, facilitating broader adoption across various defense platforms. Forward-thinking defense strategies are increasingly incorporating smart materials for defense applications to build more responsive and sustainable systems. Additionally, the integration of smart materials is poised to play a crucial role in the development of autonomous vehicles and drones, with implications for surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat missions. These strategic developments underscore the transformative potential of smart materials, setting the stage for a new era in defense capabilities.
Smart Materials in Technological Innovations
In recent years, smart materials for defense applications have moved beyond experimental phases, finding real-world applications in technological innovations that enhance military effectiveness. The versatility of these materials allows for the creation of systems that can adapt to changing environments and operational demands. Such innovations include the design of flexible armor that can adjust its rigidity based on threat levels, providing soldiers with both mobility and protection. Additionally, smart textiles embedded with sensors are being developed for uniforms that can monitor physiological conditions, ensuring the well-being of personnel in the field. The integration of smart materials is critical to advancing technological innovation in military operations.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
The development and deployment of smart materials for defense applications inevitably raise ethical and environmental considerations. The production of these materials involves resource extraction and energy use, which require sustainable practices to mitigate environmental impacts. Additionally, the ethical implications of smart material technology, particularly in terms of privacy and security, must be carefully managed. Ensuring that smart materials enhance rather than compromise global security and environmental integrity is essential. By prioritizing ethical standards and sustainability, the defense industry can responsibly harness the power of smart materials to bolster defense capabilities and global stability.
Summary and Conclusion
In summary, smart materials for defense applications represent a transformative shift in military technology. These materials offer adaptive, multifunctional properties that can significantly enhance defense systems’ resilience and efficiency. Their potential applications, ranging from adaptive camouflage to robotic enhancements, are vast and diverse. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming challenges such as cost and durability while prioritizing ethical and environmental considerations. As the defense landscape continues to evolve, the strategic integration of smart materials will play a crucial role in shaping the future of national and international security. By leveraging collaborative efforts and prioritizing innovation, the defense sector stands to benefit immensely from the advances offered by smart materials for defense applications.