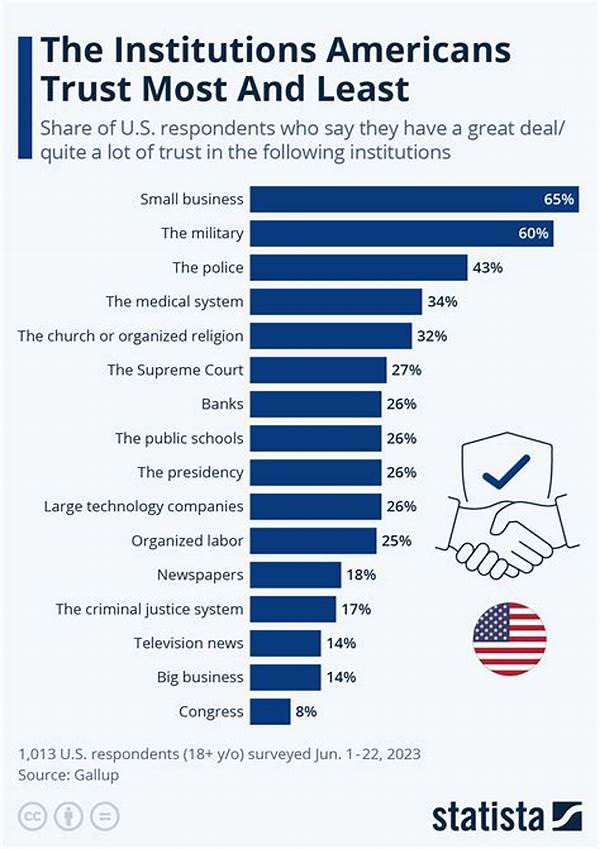
The notion of trust in media institutions is a pivotal component of society’s fabric, acting as a cornerstone in the dissemination of information. Understanding its dynamics is essential, given the profound impact media has on public opinion and democracy. When citizens place their trust in media institutions, it creates a more informed and engaged populace, enhancing societal discourse. Conversely, a lack of trust can sow doubt and misinformation, eroding the very foundation of a functional society. As we delve into this topic, we discover numerous dimensions that influence trust in media institutions, from editorial integrity to the influence of digital platforms.
The Role of Media Evolution in Trust
The evolution of media over the past few decades has significantly influenced the trust people place in these institutions. The shift from traditional print and broadcast media to a digital landscape has brought both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, the democratization of information through the internet allows for diverse voices and rapid news dissemination. However, this same development has led to the proliferation of misinformation and the rise of echo chambers, fostering environments that can both enhance and undermine trust in media institutions. As media continues to evolve, so too must our understanding of how trust is established, maintained, or lost.
Factors Affecting Trust in Media Institutions
1. Credibility of Sources: Trust in media institutions largely depends on the perceived credibility of the sources. Audiences tend to trust sources known for accuracy and reliability.
2. Editorial Independence: When media outlets maintain editorial independence, they reinforce trust in media institutions by assuring unbiased and impartial reporting.
3. Transparency in Reporting: Openly sharing the processes behind news reporting builds trust in media institutions by fostering transparency and accountability.
4. Consistency and Accuracy: Regularly delivering consistent and accurate information strengthens the public’s trust in media institutions, as it reflects a commitment to truth.
5. Engagement with Audiences: Actively engaging with audiences and addressing their concerns increases trust in media institutions, as it shows responsiveness and attentiveness to public needs.
The Impact of Digital Media on Trust
Digital media has dramatically altered the landscape of information consumption, affecting trust in media institutions. With the surge of social media platforms, news spreads faster than ever, yet not without consequences. While digital media enhances access to real-time news, it also blurs the lines between legitimate journalism and opinion. Users often struggle to discern reliable sources amidst a sea of content, thereby creating fragmented audiences with varied levels of trust in media institutions. The anonymity of online platforms further complicates trust, as users can disguise identities and motives, leading to skepticism about the authenticity of information.
Building and sustaining trust in media institutions within the digital realm requires deliberate efforts. Media organizations must prioritize transparency and rigor in verifying information before publication. Engaging with audiences to clarify and provide context also bolsters trust. Furthermore, empowering users to critically evaluate information helps foster a discerning audience capable of navigating the vast digital landscape. As technology continues to advance, so too must the strategies to cultivate and uphold trust in media institutions.
Building Trust in Media Institutions
1. Commitment to Public Interest: A steadfast commitment to serving the public good strengthens trust in media institutions, fostering a sense of reliability and integrity.
2. Fact-Checking Initiatives: Implementing robust fact-checking measures ensures accuracy and reinforces trust in media institutions by validating information.
3. Journalistic Ethics: Adhering to high ethical standards in journalism upholds trust in media institutions, promoting fairness, objectivity, and accountability.
4. Innovation and Adaptability: Embracing innovation and adapting to new technologies demonstrates a willingness to evolve, earning trust in media institutions from progressive audiences.
5. Collaborations with Experts: Partnering with subject-matter experts enhances reporting quality and strengthens trust in media institutions through informed perspectives.
6. Positively Addressing Feedback: Constructively engaging with criticism enhances trust in media institutions by demonstrating openness and a commitment to improvement.
7. Investment in Investigative Journalism: Prioritizing in-depth investigative journalism reaffirms the role of media as a watchdog, bolstering trust in media institutions.
8. Education on Media Literacy: Promoting media literacy education empowers audiences, fostering critical thinking skills and enhancing trust in media institutions.
9. Global Collaboration: Engaging in cross-border journalism initiatives strengthens trust in media institutions by providing diverse and comprehensive perspectives.
10. Sustained Community Involvement: Building relationships with local communities strengthens trust in media institutions through direct engagement and accountability.
The Relationship Between Media Trust and Public Opinion
The relationship between media trust and public opinion is complex and dynamic. Trust in media institutions plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion, as individuals often rely on trusted sources to form their perceptions and beliefs. When media outlets are perceived as trustworthy, they exert considerable influence over public discourse and decision-making processes. This trust enhances the media’s ability to introduce and explore critical issues, facilitate informed debates, and hold powerful entities accountable. Therefore, the interplay between media trust and public opinion cannot be understated, as it underpins democratic engagement and informed citizenship.
The converse is also true; public opinion can significantly impact trust in media institutions. Widespread skepticism or distrust in media can lead to declining consumption of mainstream news and increased reliance on alternative sources, some of which may lack credibility. This shift can further polarize public opinion and contribute to societal division. Ultimately, maintaining a robust trust in media institutions is essential for fostering a healthy exchange of ideas and sustaining an informed public, which is foundational to a vibrant democracy.
Strategies to Enhance Trust in Media Institutions
Enhancement of trust in media institutions necessitates multifaceted strategies and collective efforts. One crucial strategy is emphasizing transparency in journalistic practices. By openly sharing the decision-making processes behind reporting and acknowledging errors, media organizations can build stronger bonds of trust with their audiences. Implementing rigorous fact-checking protocols is another essential approach, ensuring that the information disseminated is verified and credible.
Furthermore, engaging in community outreach and encouraging audience participation in news processes strengthens trust in media institutions by demonstrating a commitment to serving public interests. Educating the public on media literacy plays a pivotal role as well, empowering individuals to critically analyze information and discern credible sources amidst the noise. Finally, embracing technological advancements while safeguarding journalistic integrity fosters adaptability and innovation, earning trust from tech-savvy audiences. Uniting these strategies fosters a resilient media landscape, conducive to cultivating lasting trust in media institutions.
Conclusion on Trust in Media Institutions
In conclusion, trust in media institutions is a critical element of a functioning democracy and informed society. The ability of media to shape public opinion, hold power to account, and facilitate public discourse hinges on the trust it garners from its audience. As media landscapes continue to evolve, maintaining this trust requires a concerted effort by media organizations to adhere to ethical standards, prioritize accuracy, and engage with their communities.
Moreover, the public plays a vital role in this dynamic, requiring media literacy to navigate and discern reliable information. As both media institutions and audiences adapt to the rapid changes brought about by digital platforms and global interconnectedness, sustaining trust becomes increasingly complex yet essential. By upholding journalistic integrity, embracing transparency, and committing to ongoing dialogue with audiences, media institutions can reinforce the trust necessary for a vibrant, informed, and engaged society.