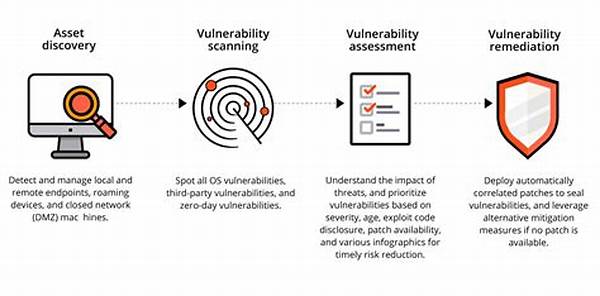
In the rapidly evolving landscape of information technology, ensuring the security of networks and systems has become more critical than ever. Vulnerability assessment and remediation is an integral process for organizations aiming to protect sensitive information and maintain operational integrity. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, this process helps identify potential weaknesses and mitigate risks effectively. By adopting a structured approach to assessing and remediating vulnerabilities, organizations can enhance their security posture and safeguard against potential breaches.
The Significance of Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
Vulnerability assessment and remediation play a pivotal role in the security management strategy of any organization. The assessment involves a systematic review of an information system’s security posture. Through this process, known vulnerabilities are identified, categorized, and evaluated based on their potential impact. Following the assessment, remediation efforts are initiated to address these identified vulnerabilities. This may include patching software, configuring security settings properly, or enhancing existing security measures. Effective vulnerability assessment and remediation not only help in closing security gaps but also contribute to the organization’s capability to predict and prevent future incidents. Ultimately, this systematic approach supports the maintenance of trust with stakeholders by ensuring that sensitive data and resources are consistently protected.
Key Components of Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
1. Identification: The first step involves discovering potential vulnerabilities within systems and networks. This typically involves using tools and techniques to scan infrastructure for weaknesses.
2. Evaluation: After identifying vulnerabilities, each is evaluated concerning its potential impact on the organization. This prioritizes the remediation process.
3. Remediation: This step involves addressing the identified vulnerabilities. Actions may include deploying patches, altering configurations, or reinforcing policies.
4. Verification: After remediation efforts, it is crucial to verify that vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed. This ensures that remediation actions have been successful.
5. Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of vulnerability assessments and remediation efforts is vital. This documentation can serve as a reference for future assessments and compliance audits.
Implementing an Effective Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation Strategy
Implementing an effective vulnerability assessment and remediation strategy requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations should integrate vulnerability assessment into their regular security operations to maintain continuous vigilance. It is essential to employ automated tools that can efficiently scan and identify vulnerabilities across various layers of the IT infrastructure. Additionally, collaboration between various departments is vital to ensure that vulnerability findings are promptly addressed. Regularly updating these tools and methodologies is necessary to keep pace with the ever-changing threat landscape.
Furthermore, training and awareness programs for employees can empower them to recognize potential vulnerabilities and report suspicious activities. It ensures that the human factor in the security equation is strong and resilient. Finally, maintaining open channels of communication with vendors and external partners can provide crucial updates and patches quickly. This cooperation can significantly enhance the timeliness and efficiency of the remediation process.
Challenges in Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
1. Resource Constraints: Limited financial and human resources can hinder the ability to perform thorough vulnerability assessments and prompt remediations.
2. Complexity of IT Environment: Diverse and complex network infrastructures can complicate the process of identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
3. Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are constantly changing, necessitating continuous updates to vulnerability assessment and remediation strategies.
4. Prioritization: Determining which vulnerabilities require immediate remediation can be challenging without a structured risk assessment framework.
5. Organizational Buy-in: Gaining support from leadership and all levels of the organization is essential for the effective deployment of vulnerability assessment and remediation initiatives.
6. Compliance Requirements: Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards can add an additional layer of complexity to vulnerability management processes.
7. False Positives in Scans: Handling false positives generated by automated vulnerability scanning tools can be time-consuming and may divert critical resources.
8. Integration with Legacy Systems: Vulnerability assessment and remediation efforts can face friction when dealing with outdated legacy systems that are difficult to upgrade or patch.
9. Third-Party Vulnerabilities: Managing vulnerabilities that exist within third-party applications or components can complicate the remediation process.
10. Change Management: Implementing remediation measures can sometimes disrupt business operations, requiring careful change management strategies.
Continuous Improvement in Vulnerability Management
Continuous improvement in vulnerability assessment and remediation necessitates a commitment to regular review and enhancement of processes. By conducting routine audits and assessments, organizations can identify areas for improvement and stay ahead of emerging threats. Leveraging insights from past incidents and assessments to refine vulnerability management processes ensures that the organization is learning and evolving. Establishing benchmarks and metrics for vulnerability management performance can further assist in evaluating the effectiveness of these efforts over time.
To support continuous improvement, organizations should foster a culture of security awareness and encourage proactive risk management. Engaging in industry collaborations and sharing best practices can provide fresh insights and innovative approaches to vulnerability management. Moreover, embracing technological advancements such as machine learning and AI can optimize vulnerability assessment and remediation, offering quicker, data-driven responses to potential threats.
Future Trends in Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
As technological advancements continue to shape the future of cybersecurity, the field of vulnerability assessment and remediation is likely to evolve accordingly. One future trend is the increasing reliance on artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of vulnerability identification and remediation. These technologies hold the promise of reducing false positives and providing more precise threat assessments. Furthermore, the growing adoption of cloud services and the Internet of Things (IoT) will necessitate a reevaluation of existing vulnerability assessment and remediation methodologies, ensuring they remain effective in increasingly distributed and interconnected environments.
The integration of advanced analytics and predictive modeling will become more prevalent, allowing organizations to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and threats before they materialize. This proactive approach will enable the development of preemptive remediation strategies, thereby minimizing the risk of exploitation. As the complexity of cyber threats continues to grow, future vulnerability management strategies will require a more agile and adaptive framework, emphasizing collaboration across all levels of an organization.
Summary of Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation
In summary, vulnerability assessment and remediation are crucial components of an organization’s cybersecurity framework. These processes allow for the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of potential security risks, thereby fortifying the organization’s defenses against cyber threats. By systematically addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can reduce the likelihood of breaches and enhance their overall security posture. Effective implementation of vulnerability assessment and remediation involves not only the technical assessment of systems but also the involvement of human resources and organizational processes to ensure a comprehensive security strategy.
The continuous evolution of cyber threats necessitates an adaptive approach to vulnerability management. Organizations must remain vigilant, integrating the latest technological advancements and industry best practices into their security protocols. By fostering a culture of security awareness and collaboration, organizations can ensure that they are well-equipped to handle current and emerging security challenges. In conclusion, vulnerability assessment and remediation form the cornerstone of a resilient cybersecurity strategy, enabling organizations to protect their assets, maintain stakeholder trust, and meet the ever-growing demands of the digital age.